Figure 4.
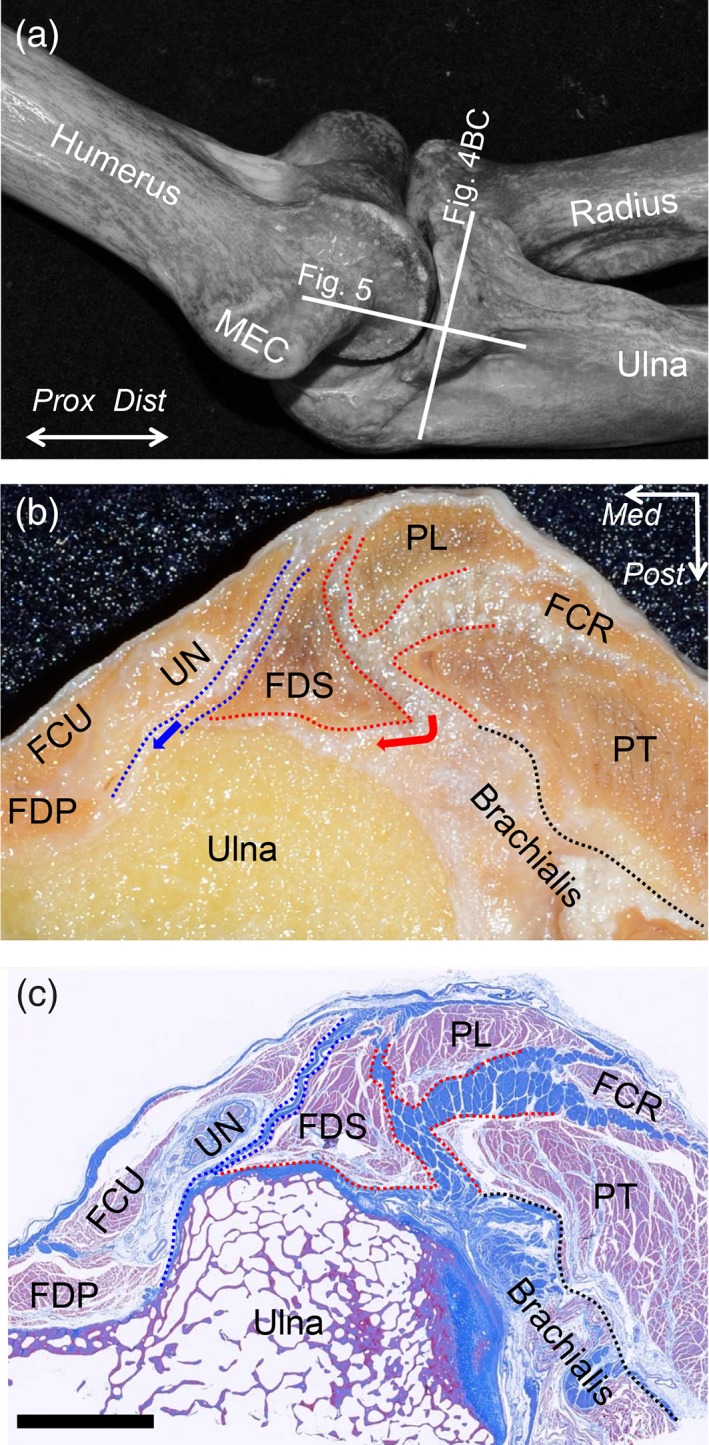
Histological analysis of the axial section at the sublime tubercle. (A) Locations of the histological section in Figs. 4 and 5 are indicated as white lines on the bony scheme of the medial aspect of the left elbow. (B) The macroscopic view of the axial section at the level of the ST is shown as the white line in A. (C) Masson's trichrome staining of the section is shown in (B). The TS between the PT and FDS muscles was densely stained (red dotted area), connected to the intramuscular tendon of the brachialis muscle (black dotted line), and transitioned into the deep FDS aponeurosis (red arrow). The TS between the FDS and FCU muscles was also identified (blue dotted area) and continued into the deep FCU aponeurosis (blue arrow). These two TS, the intramuscular tendon of the brachialis muscle, and the deep aponeuroses of the FDS and FCU muscles were connected and formed the tendinous complex. FCR, flexor carpi radialis; FCU, flexor carpi ulnaris; FDP, flexor digitrum profundus; FDS, flexor digitrum superficialis; MEC, medial epicondyle; PT, pronator teres; PL, palmaris longs; UN, Ulnar nerve; Dist, distal; Prox, proximal; Med, medial; Post, posterior, Scale bar, 5 mm [Color figure can be viewed at https://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
