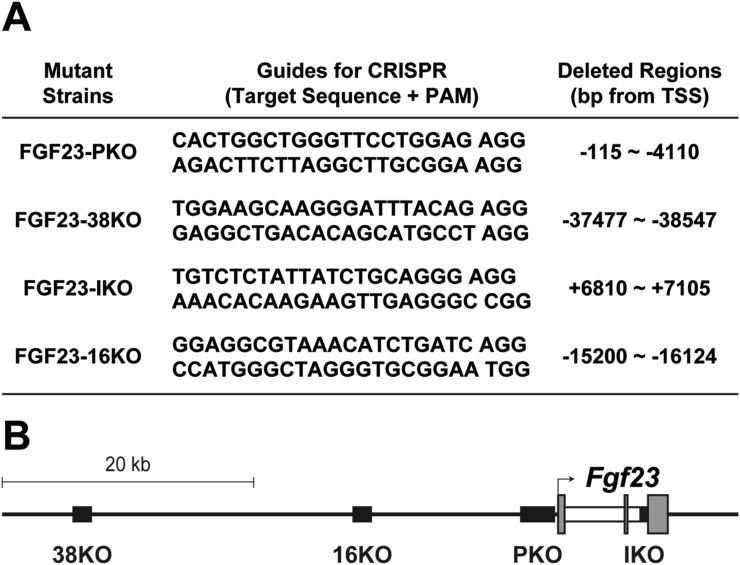
Figure 1.
Generation of Fgf23-enhancer mutant mouse strains. (A) Putative Fgf23 enhancers epigenetically identified by chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by DNA sequencing (ChIP-seq) analyses were individually deleted to create the mouse strains indicated. Sequences of the guide RNAs used for the CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing method for each mutant are documented. Genomic locations of the deleted region in each mouse strain were determined by sequencing and are provided. FGF23-16KO mouse strain was previously generated (31). (B) Illustration of the Fgf23 gene locus in the mouse. Relative locations of the deleted regions in FGF23-PKO (PKO), FGF23-38KO (38KO), FGF23-IKO (IKO), and FGF23-16KO (16KO) mouse strains are displayed as black boxes. Exons and introns of Fgf23 gene are represented by gray and white boxes, respectively. Transcription start site is marked as an arrow. PAM, Protospacer adjacent motif; TSS, transcription start site.