Figure 1.
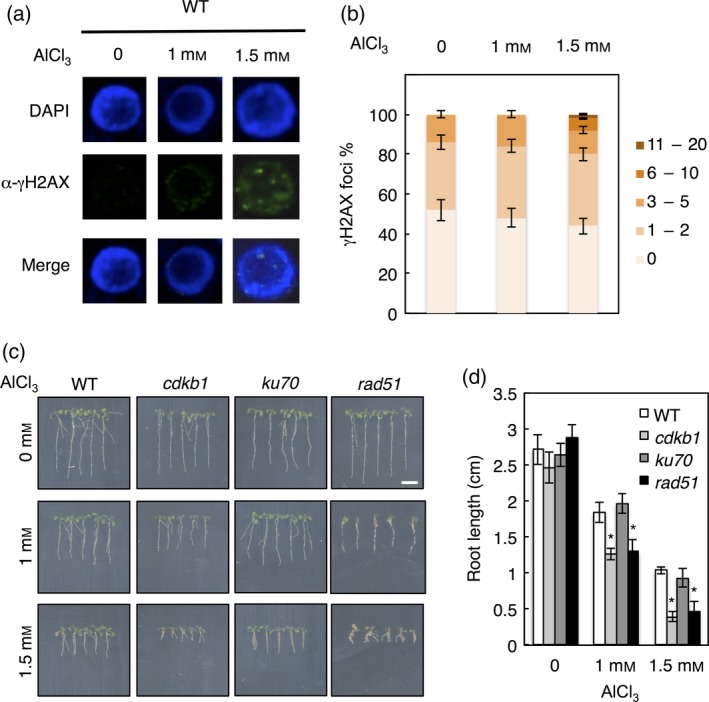
Detection of Al‐induced DNA damage in long‐term growth assays.
(a) Immunofluorescence analysis of γH2AX accumulation (green) in DAPI‐stained nuclei (blue) of wild‐type (WT) Arabidopsis root tips grown for 10 days on Al‐containing medium. (b) Quantification of γH2AX foci in WT plants after Al treatment. One‐hundred nuclei per line per experiment were grouped into six classes according to their number of γH2AX foci: nuclei containing no γH2AX foci, 1–2, 3–5, 6–10 and 11–20 γH2AX foci. (c) Seedling growth of WT, cdkb1, ku70 and rad51 mutants. Seeds were germinated on soaked gel medium containing 0, 1 and 1.5 mm Al (pH 4.2), and grown for 10 days. Scale bar: 1 cm. (d) Root growth measurements of WT, cdkb1, ku70 and rad51 mutants grown on soaked gel medium containing 0, 1 and 1.5 mm Al (pH 4.2) for 10 days. Data are presented as mean ± SD in three independent experiments. Significant differences from WT were determined by independent samples t‐test: *P < 0.05.
