Figure 3.
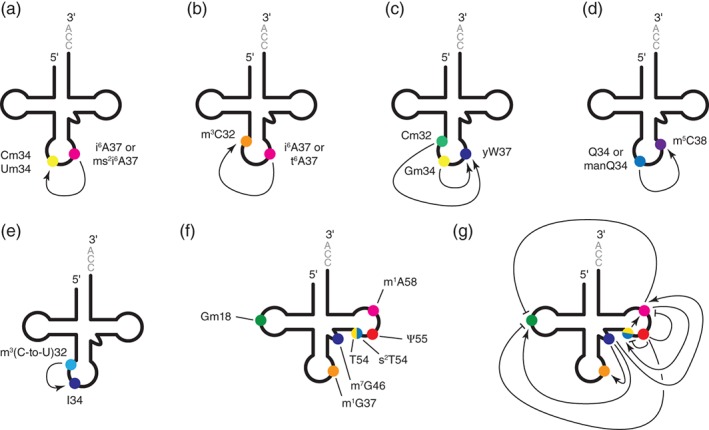
Modification circuits in tRNAs. (a–e) Modification circuits found in the anticodon‐loop region. (a) i6A37 or ms2i6A37 stimulate Um34 and Cm34 formation in E. coli tRNALeu(UAA) and tRNALeu(CAA). (b) i6A37 stimulates m3C32 formation in tRNASer of S. pombe and S. cerevisiae and t6A37 stimulates m3C32 formation in tRNAThr of S. cerevisiae. (c) Cm32 and Gm34 stimulate wybutosine yW37 formation in eukaryotic tRNAPhe. (d) Queuosine Q34 or mannosyl–queuosine manQ34 stimulate m5C38 formation in tRNAAsp of several organisms (see text). (e) m3U32 originating from m3C32 stimulates I34 formation in T. brucei tRNAThr(AGU). (f, g) An intricate modification network in T. thermophilus. (f) The modifications involved in the modification network in T. thermophilus are represented on the cloverleaf representation of tRNA with filled colored circles. Gm18 is shown in green, m1G37 in orange, m7G46 in purple, T54 and s2T54 as half‐filled circles in yellow and blue, respectively, Ψ55 in red, and m1A58 in pink. (g) An intricate modification network in T. thermophilus enables the adaptation of tRNA modifications in response to temperature changes. The same color code is used as in panel (f). Arrows indicate stimulatory effects and blunted lines inhibitory effects.
