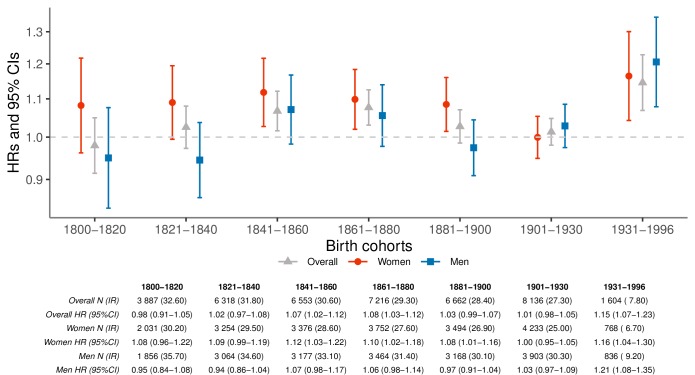
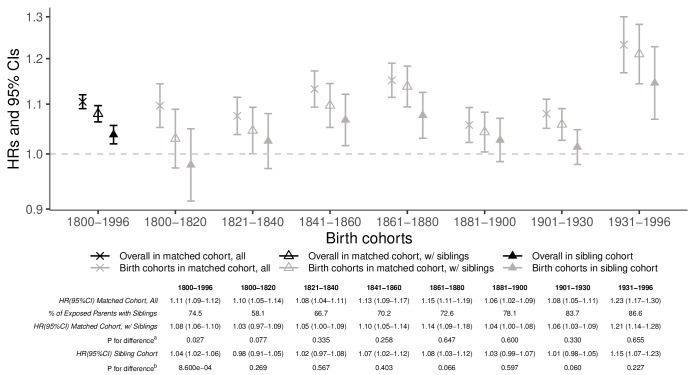
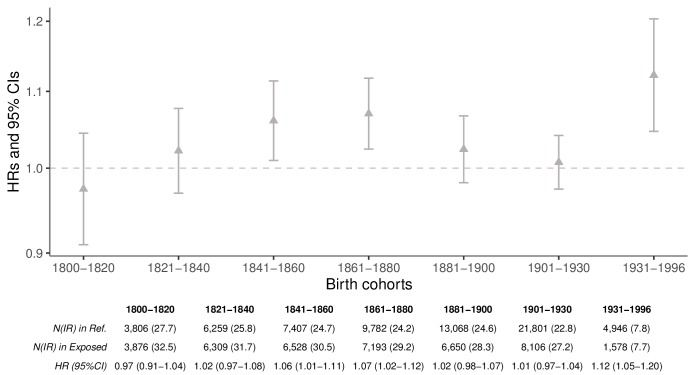
Figure 1. Hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of parental mortality after loss of a child by birth cohorts (every 20 years until 1900, 1901–1930, and 1931–1996), in the sibling cohort.
We estimated HRs from stratified Cox proportional hazards model using age as underlying time scale. We stratified by sibling groups and additionally adjusted for birth year and sex. IR, incidence rate, per 1000 person-years.