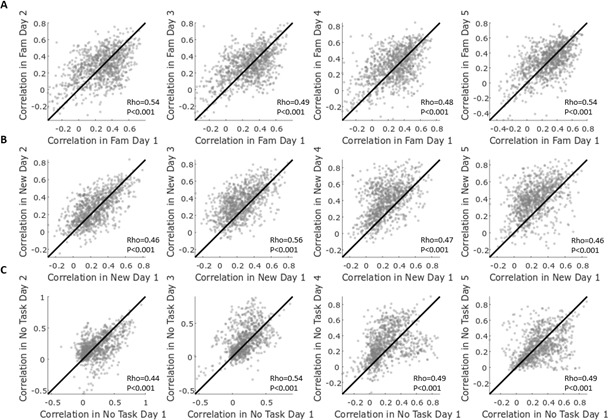
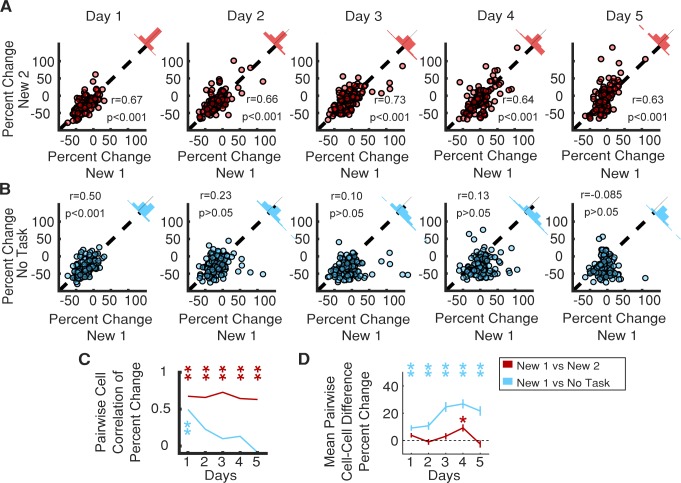
Figure 6. Consistent SOM-int activity responses across different new environments and in ‘No Task’ epoch.
(A) Individual SOM-ints show correlation in activity modulation in two distinct New environments. (B) Similar correlation of activity modulation is seen between New 1 and ‘No Task’ exposures for Day 1. On subsequent days, correlation disappears as SOM-int activity begins to return in New 1 while remaining suppressed in ‘No Task’. (C) Summary of correlation data from (A) and (B). Correlation between percent change of cells between two remapping sessions or between remapping session one and the ‘No Task’ exposure session. (D) Mean difference in percent change in activity in cells between remapping and ‘No Task’ exposure settings (*p<0.01, **p<0.001, one-sample t-test with Bonferroni-Holm correction N = 6, n = 116).
Figure 6—figure supplement 1. Characterization of suppressed SOM-ints.
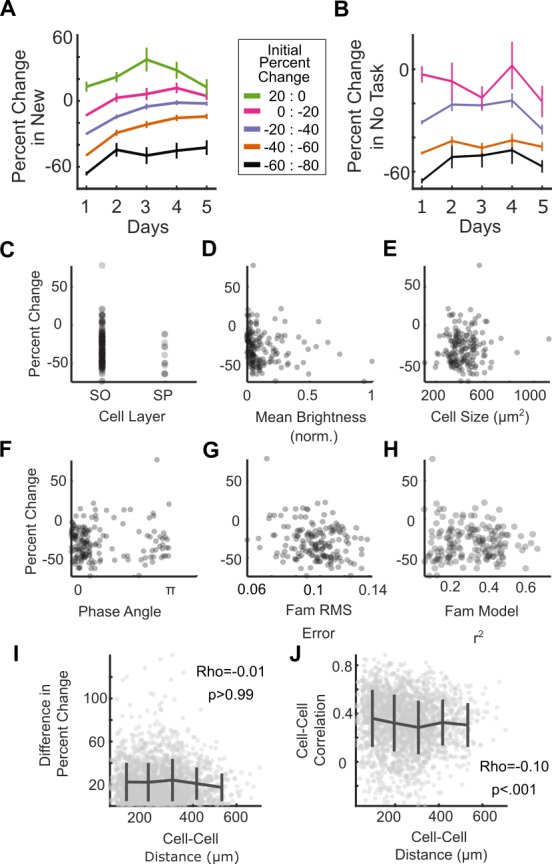
Figure 6—figure supplement 2. SOM-int network activity structure is stable across environments.
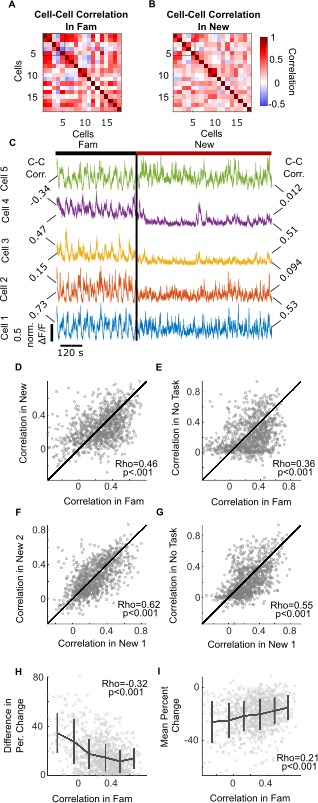
Figure 6—figure supplement 3. SOM-int network activity structure is stable across days in the same environment.