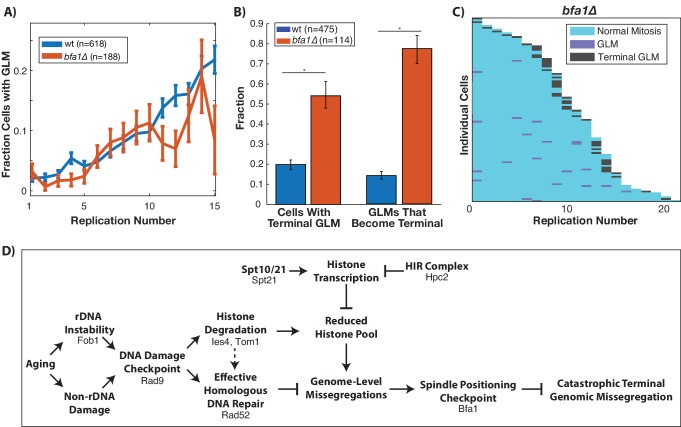
Figure 7. Correction of GLM events requires the spindle positioning checkpoint.
(A) Removal of BFA1 disrupts the spindle positioning checkpoint, but fails to abolish an increase in GLMs during aging (curve shows mean and error bars are SEM, p<0.05 determined by Cochran Q-test). Lifespan only shown 0–15 divisions due to reduced lifespan of bfa1∆ mutants. (B) Compared with wildtype, a bfa1∆ strain has significant increases in both the fraction of cells that experience terminal missegregations and the likelihood that an individual GLM will become terminal. Error bars that do not overlap show significance at the p=0.05 level and were generated by bootstrapping with replacement. N values are number of cells. (C) The difference in bfa1∆ GLM dynamics is stark at the single cell level where most GLMs result in terminal missegregations and most mother cells die because of terminal GLMs. Each row is a separate mother cell, and the color indicates whether a cell experienced a normal cell cycle, GLM or terminal missegregation (n = 100 randomly selected cells). (D) Model for age-associated GLMs that links age associated changes in DNA damage to failures during mitosis. Proteins included in the diagram at each stage are those that have been genetically perturbed in this work.