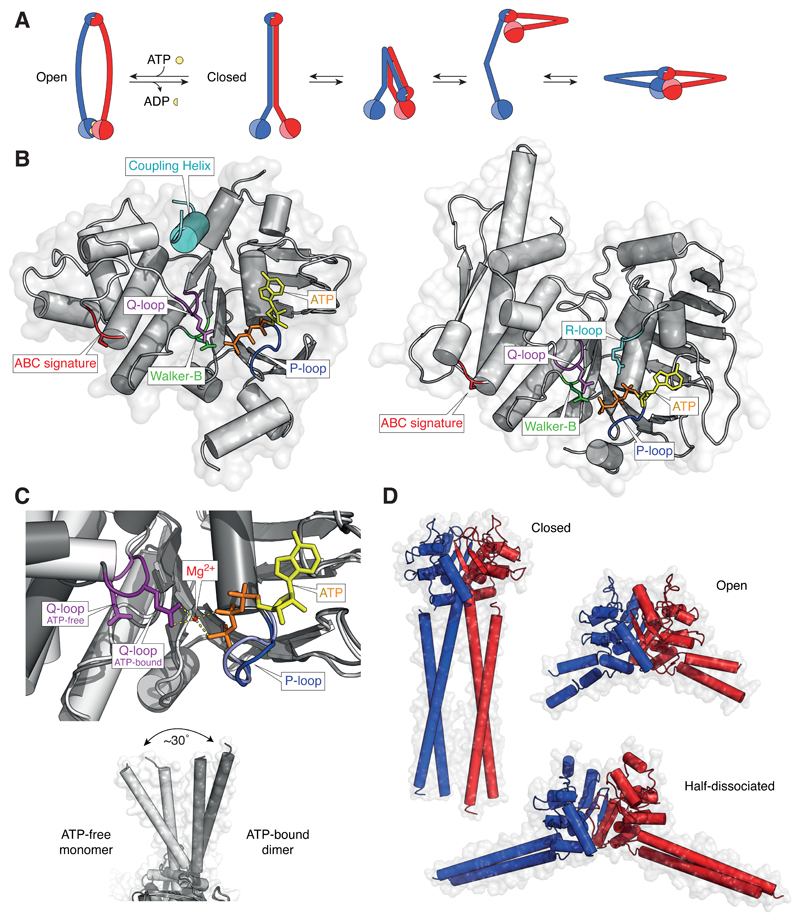
Figure 4. Conformational changes in SMC proteins.
(A) Models of ATP-bound open (ring-shaped) and ATP-free closed (rod-shaped) SMC dimers and conformational transitions of condensin SMC subunits observed in AFM images. (B) Structure models of the ATP-bound NBD of the Staphylococcus aureus Sav1866 ABC transporter ATPase (pdb: 2onj) and of the Geobacillus stearothermophilus SMC ATPase head domain (pdb: 5h68). (C) Close-up view of the Q-loop conformation in structures of the ATP-free monomeric B. subtilis SMC ATPase head domain (light grey; pdb: 5h67) and the ATP-dimerized B. subtilis SMC ATPase head domain (dark grey; pdb: 5xg3) and side-views of the coiled-coil orientations in both structures. (D) Structural models of the Pyrococcus furiosus SMC hinge domain in the closed coiled-coil conformation (pdb: 4rsj), of the T. maritima SMC hinge domain in the open coiled-coil conformation with both hinge interfaces associated (pdb: 1gxl) and of the G. stearothermophilus SMC hinge domain in the open coiled-coil conformation with one hinge interface dissociated (pdb: 5h69).