Figure 6.
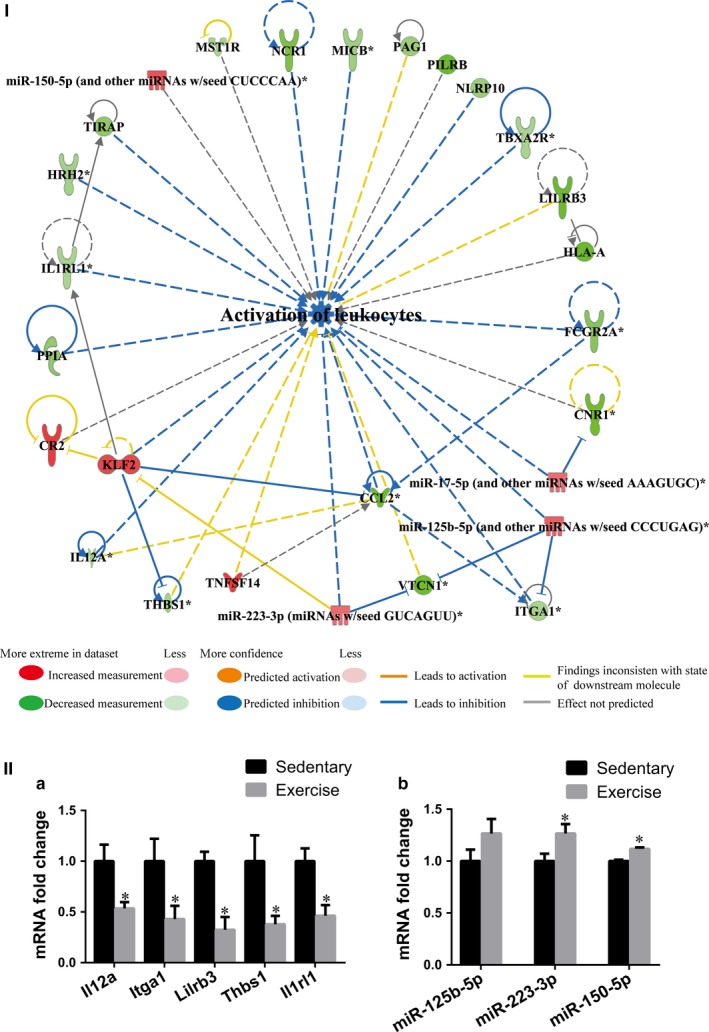
Inhibition of leucocyte activation played a role in the early moderate exercise‐mediated improvement of inflammation. (I) The integrated ingenuity pathway analysis between miRNAs and mRNAs predicted that the activation of leucocytes in the infarct zone was decreased (P‐value = 3.51E‐04; z‐score = −2.209) in the early moderate exercise MI heart compared with the sedentary MI heart. The regulatory network demonstrates that 27 molecules (20 down‐regulated genes, 3 up‐regulated gene and 4 up‐regulated miRNAs) were included in the regulatory network for the decreased activation of leucocytes. The directive inhibition relationship, which included miR‐125b‐5p for ITGA1, FCGR2A for CCL2 and KLF2 for CCL2, was shown to be associated with the inhibition of leucocyte activation. (II) The qPCR quantifications of the expression levels of selected genes included in the decreased activation of the leucocyte network and decreased leucocyte migration network (Figure 7). (a) Selected genes. (b) Selected miRNAs. The animals were trained on the early moderate exercise for two weeks beginning one day after MI. n = 3 per group. *P < .05 vs the sedentary group
