Figure 2.
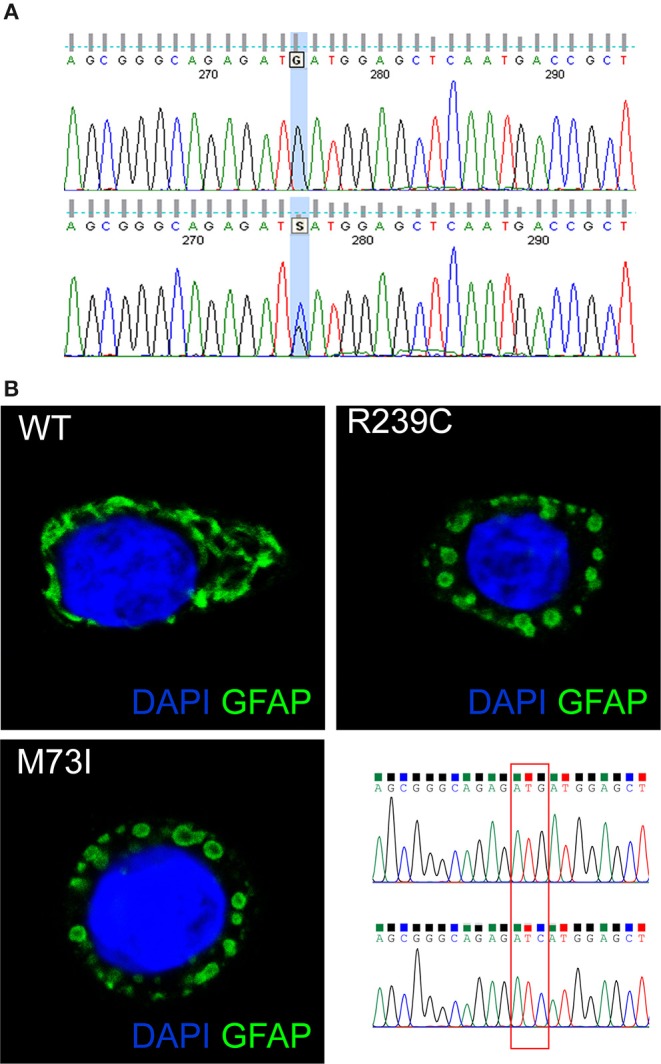
(A) The GFAP exon 1 sequence, obtained from a control (top) and our patient (bottom). The bottom picture shows heterozygosity for the missense c.219G>C nucleotide change, corresponding to the p.M73I mutation. (B) Representative images showing HeLa cells transiently transfected with plasmids encoding human wild-type GFAP or mutant GFAP M73I and R239C and labeled with GFAP antibody. The image shows wild-type GFAP assembled in filament networks, whereas mutant M73I and R239C formed dot-like aggregates. On the right, a detail is given of the Sanger sequences of the plasmids encoding wild-type GFAP and GFAP M73I; codon 73 was mutated from ATG (Met) to ATC (Ile).
