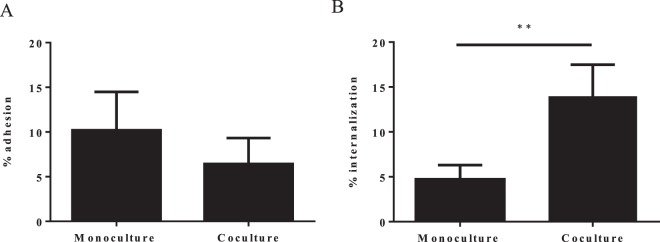
Figure 9.
S. aureus internalization is increased within A549 epithelial pulmonary cells in the presence of P. aeruginosa. (A) Adhesion of S. aureus onto epithelial cells. A549 cells were infected at MOI 10:1 for S. aureus monoculture and 20:1 for S. aureus/P. aeruginosa coculture. After 2 hours of contact, cells were washed with phosphate buffer saline (PBS) to remove unattached bacteria and lysed with sterile water. Supernatants were plated on MSA to count S. aureus. The results are represented as the percentage of inoculum that adhered. (B) Internalization of S. aureus within epithelial cells. After 2 hours of contact, cells were treated with antibiotics and lysostaphine for one hour, lysed with sterile water and bacteria plated on MSA. The results are represented as the percentage of adhered cells that have internalized. All values represent the mean + standard deviation from three independent experiments with three strain pairs (SA27-PA27, SA31-PA31 and SA69-PA69). Statistical significance was determined by unpaired t-test (**P < 0.01).