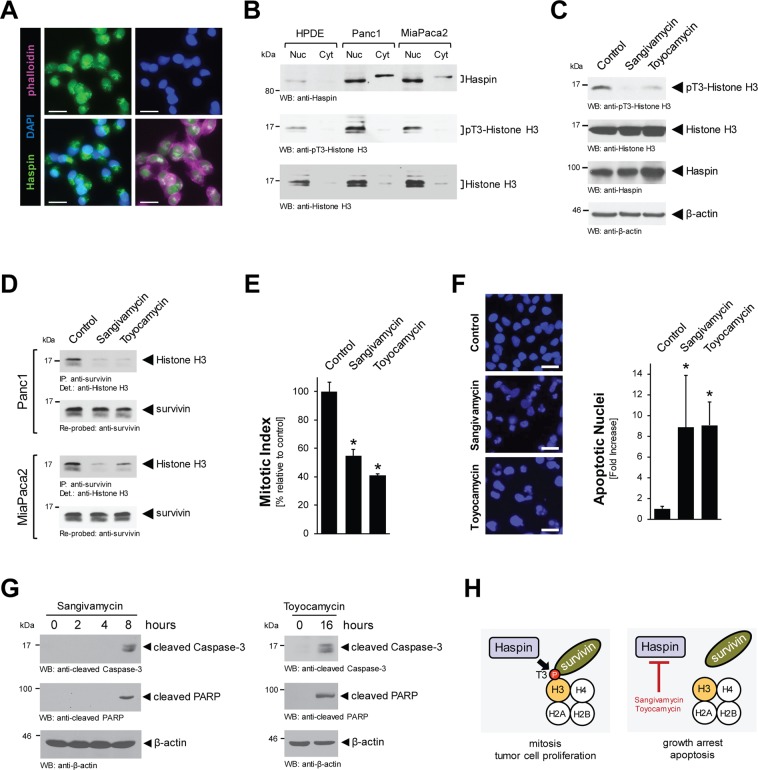
Figure 4.
Sangivamycin and Toyocamycin target Haspin-pT3-Histone H3 signaling. (A) Localization of endogenous Haspin was determined in Panc1 cell by immunofluorescence with anti-Haspin antibody and co-staining with DAPI (nuclei) and phalloidin (cytoskeletal structures). The bar represents 25 µm. (B) Nuclear and cytoplasmic cell fractions were analyzed by Western blot for expression of Haspin (anti-Haspin), phosphorylated Histone H3 (anti-pT3-Histone H3) and total Histone H3. (C) Panc1 cells were stimulated for 16 hrs with 500 nM Sangivamycin or Toyocamycin. Whole cell lysates were analyzed by Western blot for expression of Haspin (anti-Haspin), phosphorylated Histone H3 (anti-pT3-Histone H3) and total Histone H3. Staining for β-actin served as control for equal loading. (D) Panc1 or MiaPaca2 cells were stimulated for 16 hrs with 500 nM Sangivamycin or Toyocamycin. Survivin was immunoprecipitated and samples were analyzed for co-immunoprecipiated Histone H3. (E) Panc1 cells were treated with DMSO (control), Sangivamycin (500 nM) or Toyocamycin (500 nM) for 8 hours and a Mitotic Index assay was performed. (F) Panc1 cells were stimulated for 48 hrs with 500 nM Sangivamycin or Toyocamycin as indicated. Left side: Loss of nuclear integrity, indicating apoptosis was determined using DAPI staining. The bar represents 50 µm. Right side: The bar graph shows a quantification of apoptotic nuclei for each condition. The asterisk indicates statistical significance. (G) Panc1 cell lysates were treated with Sangivamycin or Toyocamycin for indicated times. Apoptotic signaling was determined by Western blot probing for cleaved Caspase-3 and cleaved PARP. Staining for β-actin served as control for equal loading. (H) Proposed mechanism of how Sangivamycin and Toyocamycin target cell proliferation and induce apoptotic cell death.