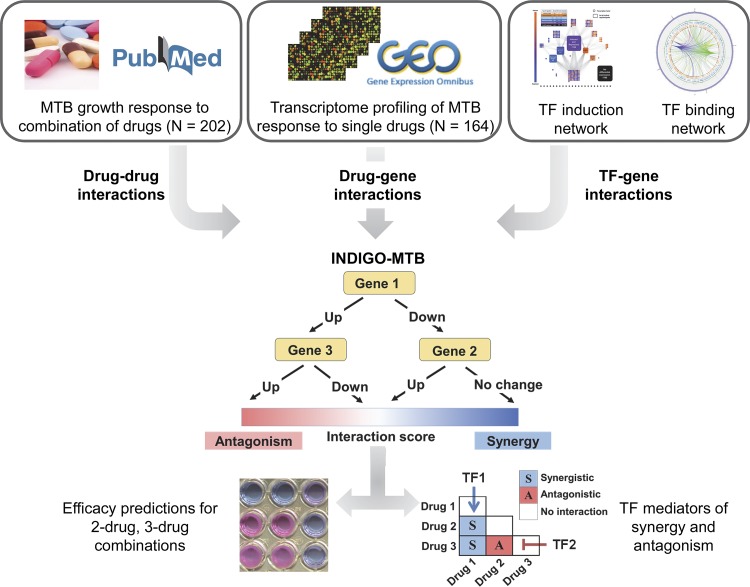
FIG 1.
Schematic of INDIGO-MTB. INDIGO uses drug-gene associations inferred from transcriptomic data and experimentally measured drug-drug interactions as inputs to train a computational model that can infer interactions between new combinations of drugs. It does this by learning patterns in the drug-gene associations that are correlated with synergy and antagonism. In the example above, MTB upregulation of both gene 1 and gene 3 in response to the drugs measured in monotherapy is predictive of antagonism when the drugs are combined. By perturbing individual genes and known targets of transcription factors (TFs) in the model, we can infer the impact of individual gene and TF activity, respectively, on drug interactions and subsequently engineer interaction outcomes.