Figure 1.
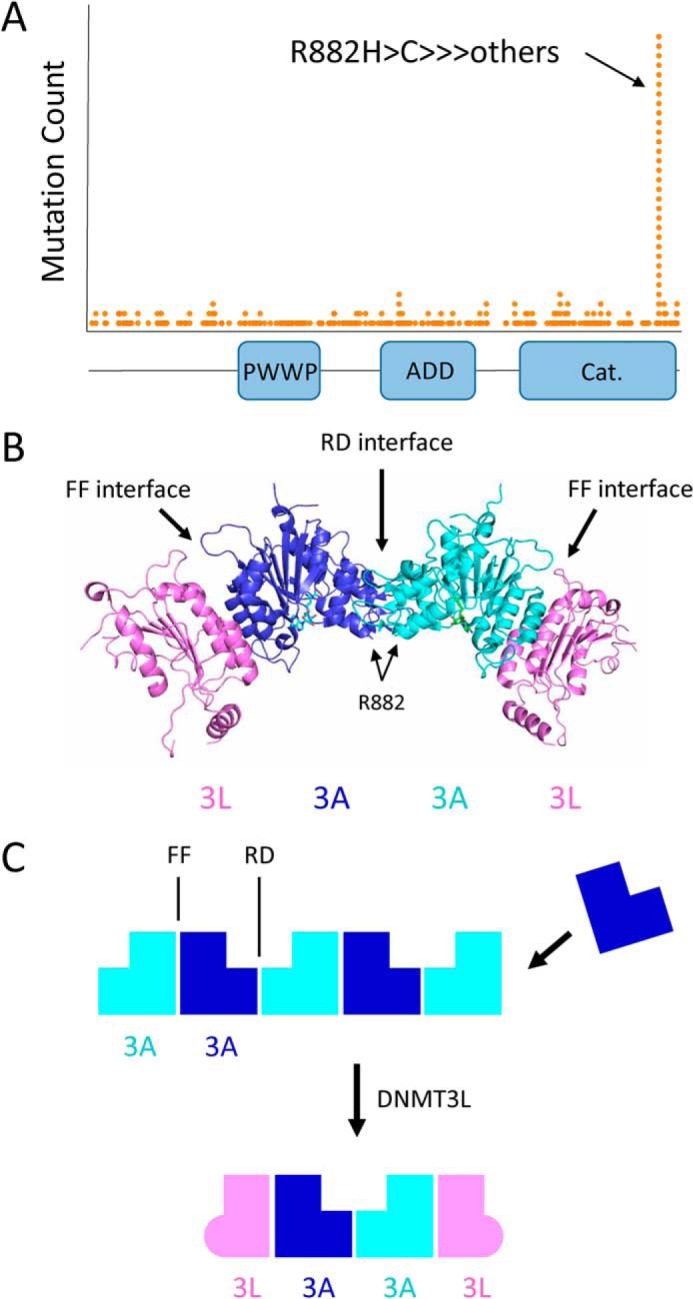
DNMT3A cancer mutations, domain architecture, and oligomer formation. A, histogram of DNMT3A mutations observed in cancer from the TCGA cohort. The R882H hot spot mutation is located at the C-terminal catalytic domain. B, crystal structure of the DNMT3L–DNMT3A–DNMT3A–DNMT3L complex (PDB code 2QRV). Arg-882 is located at the RD interface between two DNMT3A catalytic domains. C, DNMT3A catalytic domain mediates the formation of large oligomers through self-association along two binding surfaces, called the RD and FF interfaces. DNMT3L prevents the formation of large DNMT3A oligomers, instead forming a tetramer composed of two DNMT3A and two DNMT3L molecules.
