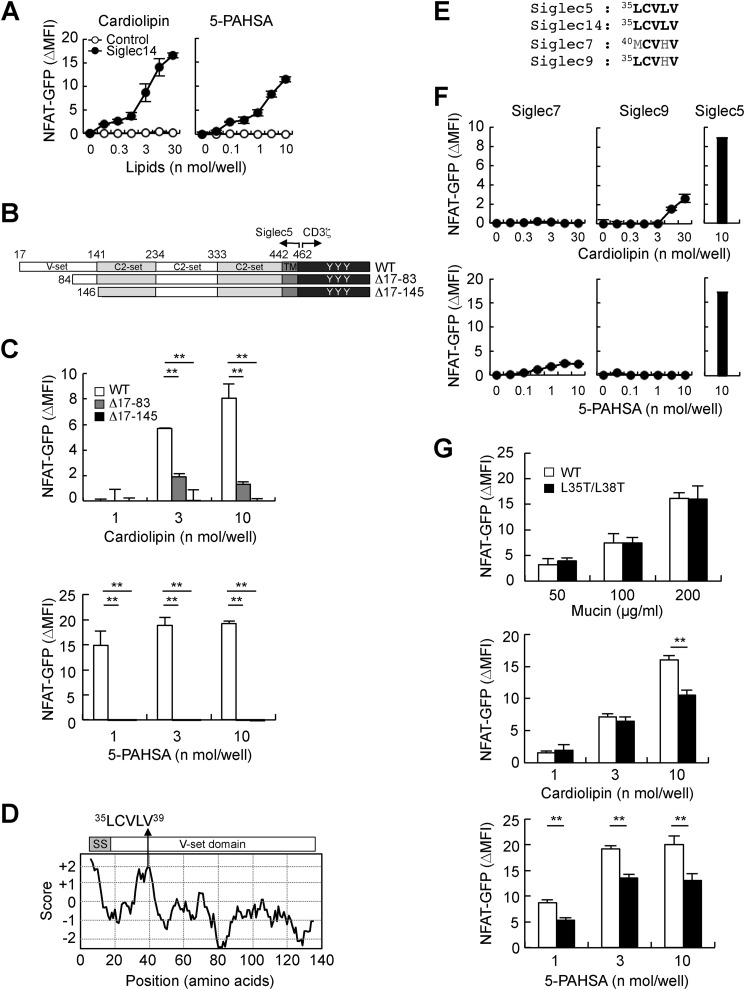
Figure 5.
The hydrophobic stretch in the N terminus of Siglec5 is required for efficient recognition of lipophilic ligands. A, Siglec14 reporter cells were stimulated with plate-coated cardiolipin or 5-PAHSA for 18 h. Induction of NFAT-GFP was analyzed by flow cytometry. B, schematic representations of N-terminal deletion mutants of Siglec5-CD3ζ chimeric receptors. C, WT and N-terminus–deleted Siglec5 reporter cells were co-cultured with plate-coated cardiolipin or 5-PAHSA. D, hydrophobicity of N-terminal region of Siglec5 was analyzed using the ExPASy-ProtScale online tool. SS, signal sequence. E, sequence alignment of hydrophobic stretches of Siglecs. F, Siglec7, -9, and -5 reporter cells were exposed to plate-coated cardiolipin or 5-PAHSA. G, Siglec5 reporter cells expressing WT and L35T/L38T mutant were stimulated with plate-coated mucin, cardiolipin, or 5-PAHSA. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments and are presented as the mean ± S.D. (error bars). **, p < 0.01.