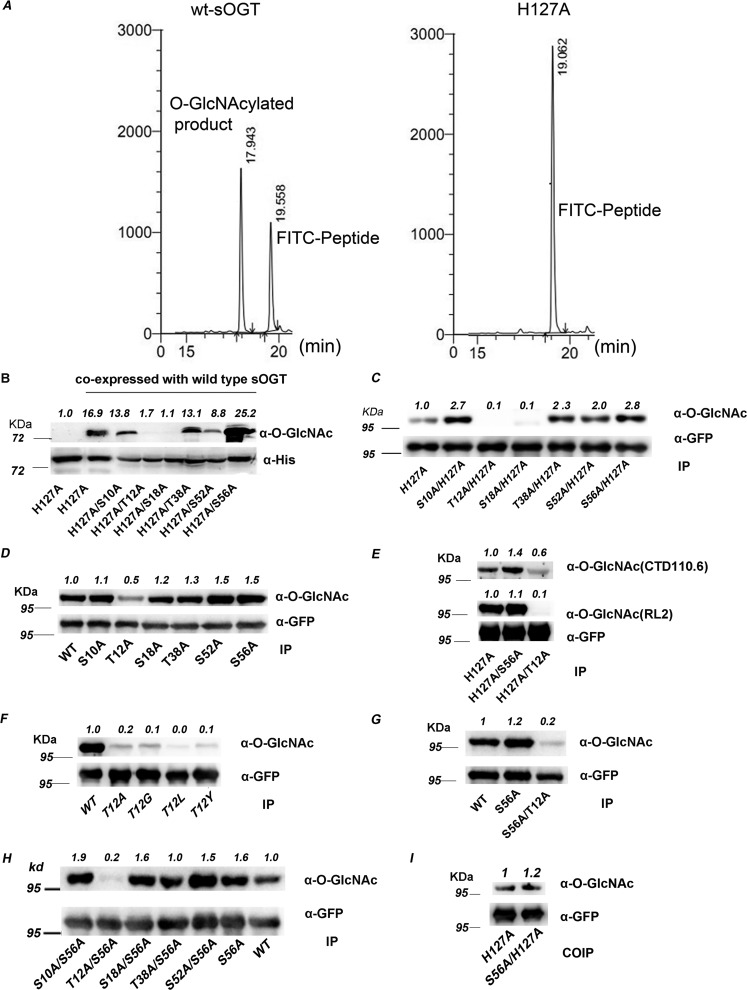
Figure 2.
Thr12 and Ser56 are two key O-GlcNAcylation sites on sOGT. A, H127A mutation abrogated sOGT activity in vitro. B, assessment of the modification sites in E. coli cells. WT sOGT was co-expressed with the indicated sOGT mutants (with an N-terminal His6 tag) in E. coli BL21 (DE3) cells. O-GlcNAcylation of the mutants was examined via Western blotting. C–H, assessment of the modification sites in HEK293T cells. The indicated sOGT mutants were expressed in HEK293T cells. O-GlcNAcylation of the mutants was examined via Western blotting. C, double-point mutants with H127A mutation. D, single-point mutants. E, O-GlcNAcylation was examined with two O-GlcNAc–specific antibodies. F, other Thr12 mutants. G, S56A and T12A/S56A. H, double-point mutants with S56A. I, each indicated mutant (H127A, T12A, or S56A) was co-expressed with WT sOGT (with an N-terminal c-Myc tag) in HEK293T cells. Co-immunoprecipitation/Western blotting was performed to examine the interaction between WT sOGT and each mutant. Western blots were quantified with ImageJ for each blot, and O-GlcNAcylation of target mutants was normalized to the input (α-His in B/α-GFP in others).