Figure 1.
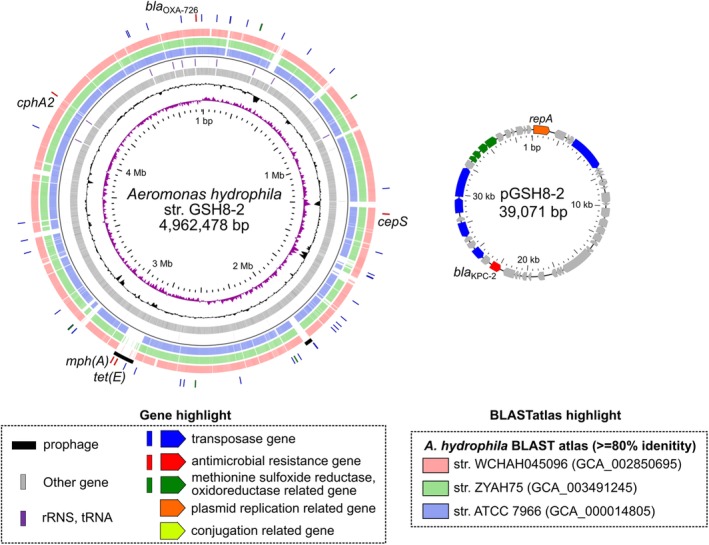
Schematic circular representation of complete genome sequences of KPC‐2‐producing A. hydrophila GSH8‐2. Short paired‐end whole‐genome sequencing was performed using an Illumina NextSeq 500 platform with a 300‐cycle NextSeq 500 Reagent Kit v2 (2 × 150‐mer). The complete genome sequences of the strains were determined using a PacBio Sequel sequencer for long‐read sequencing [Sequel SMRT Cell 1 M v2 (4/tray]; Sequel sequencing kit v2.1; insert size, approximately 10 kb). De novo assembly was performed using Canu version 1.4 (Koren et al., 2017), minimap version 0.2‐r124 (Li, 2016), racon version 1.1.0 (Vaser et al., 2017) and circulator version 1.5.3 (Hunt et al., 2015). Error correction of tentative complete circular sequences was performed using Pilon version 1.18 with Illumina short reads (Walker et al., 2014). Annotation was performed in Prokka version 1.11 (Seemann, 2014), InterPro v49.0 (Finn et al., 2017) and NCBI‐BLASTP/BLASTX. Circular representations of complete genomic sequences were visualized using GView server (Petkau et al., 2010). AMR genes were identified by homology searching against the ResFinder database (Zankari et al., 2012). The class 1 integron was assigned in the INTEGRALL database (http://integrall.bio.ua.pt/) (Moura et al., 2009). Visualization of comparative plasmid ORFs organization was performed using Easyfig (Sullivan et al., 2011). For representation of chromosomal DNA, from the inside: slot 1, GC skew; slot 2, GC content; slot 3, ORFs; slot 4, rRNA/tRNA; slots 5–7, BLASTatlas conserved gene analysis indicating three relative strains (see also Supporting Information Fig. S1); slot 8, prophage; slot 9, notable ARGs or ARG‐related genes (transposase, ARGs and reductases). In representations of circular plasmids, notable ORFs are highlighted as the indicated colour.
