Figure 7.
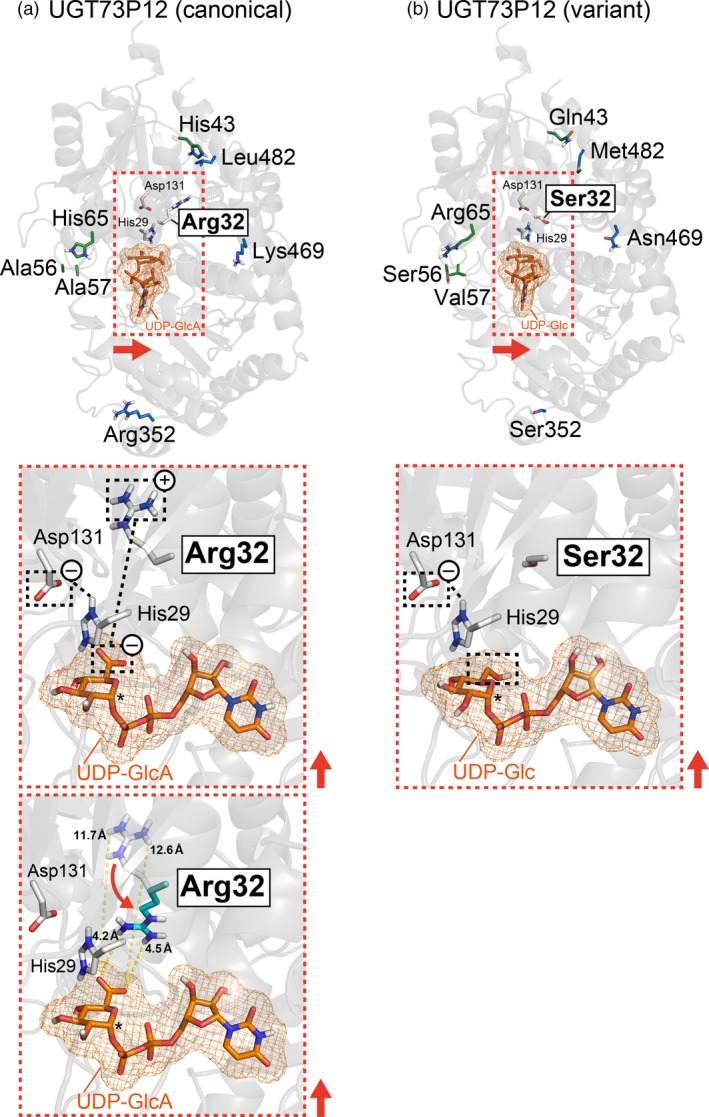
Virtual docking of UDP‐sugars onto homology models of UGT73P12 proteins.
(a) Structural model of the canonical UGT73P12 protein docked with UDP‐glucuronic acid.
(b) Structural model of variant UGT73P12 protein docked with UDP‐glucose.
UDP‐glucuronic acid and UDP‐glucose are abbreviated as UDP‐GlcA and UDP‐Glc, respectively. The side‐chains of variant amino acid residues in the canonical and variant UGT73P12 proteins are shown in white (Arg32/Ser32; N‐domain residue), green (the other N‐domain residues) or blue (C‐domain residues) on each structural model (light gray background) (upper panels). The expected positions of sugar donor pockets in each protein are shown in the orange dotted box with the catalytically essential residues, His29 and Asp131 (N‐domain residues; white). The close‐up views (middle panels) indicate the predicted spatial arrangements of the key residues (His29, Asp131 and Arg32/Ser32) and UDP‐sugars (orange) within the sugar donor pockets in each protein. Possible electrostatic interactions among the key residues and UDP‐sugars are also shown with black dotted lines. The anomeric carbon of UDP‐sugars, which is related to the UGT reaction, is shown by asterisks. The direction of the red arrows in the overview maps was used to project the close‐up views. The possible conformation change of Arg32 in the canonical UGT73P12 protein and the minimal distance between the Arg32 and UDP‐glucuronic acid are displayed in the lower panel of (a).
