Figure 5.
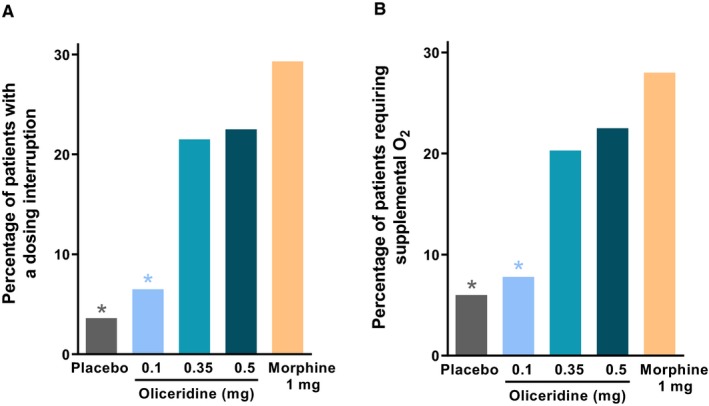
Clinical interventions. A, The proportion of patients in each regimen who experienced any dosing interruption of study medication during the study is presented. Exploratory analyses showed that the odds ratio of an interruption compared to morphine was 0.09 (P < 0.0001) for placebo, 0.15 (P = 0.0002) for oliceridine 0.1 mg, 0.57 (P = 0.13) for oliceridine 0.35 mg, and 0.64 (P = 0.23) for oliceridine 0.5 mg regimens. B, The proportion of patients in each regimen who required supplemental oxygen therapy is presented. Exploratory analyses showed that the odds ratio of an interruption compared to morphine was 0.15 (P = 0.0002) for placebo, 0.18 (P = 0.0005) for oliceridine 0.1 mg, 0.54 (P = 0.11) for oliceridine 0.35 mg, and 0.65 (P = 0.25) for oliceridine 0.5 mg regimens. *P < 0.05 odds ratio vs. morphine.
