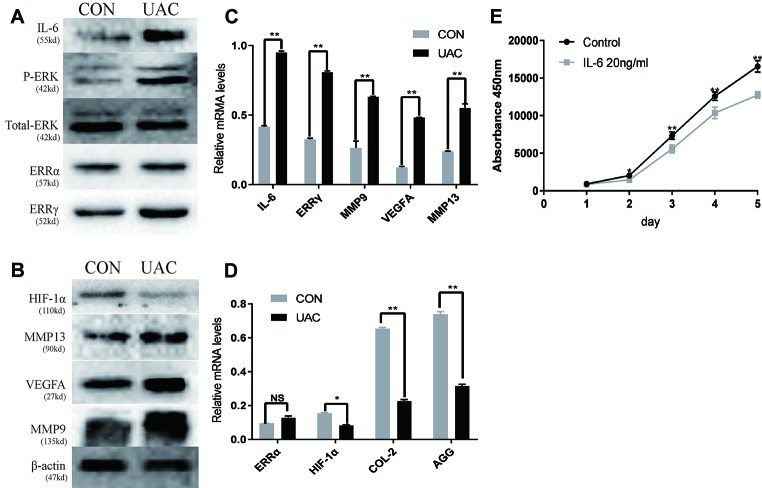
Figure 2.
The relationship between interleukin 6 (IL-6), extracellular signal–regulated kinase (ERK), estrogen-related receptor γ (ERRγ) and temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis (TMJOA). (A) and (B) Representative images of Western blot assays demonstrate the relationship between IL-6, phospho-ERK (P-ERK), ERRγ, matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9), MMP13, HIF-1α, vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA), and TMJOA, while the expression levels of total ERK and β-actin were the same in the cartilage tissues of the control group and the UAC group (n = 12 rats per group). (C) and (D) RT-qPCR analysis of IL-6, ERRγ, MMP9, MMP13 VEGFA, COL2, AGG, HIF-1α, and ERRα in cartilage tissues of the control group and the UAC group (n = 12 rats per group). (E) The CCK-8 assay was used to examine the cell proliferation of each group; the absorbance was measured at 450 nm (n = 3). All experiments were performed in triplicate, and the results are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. NS not significant. Scale bar: 50 μm.