Figure 2.
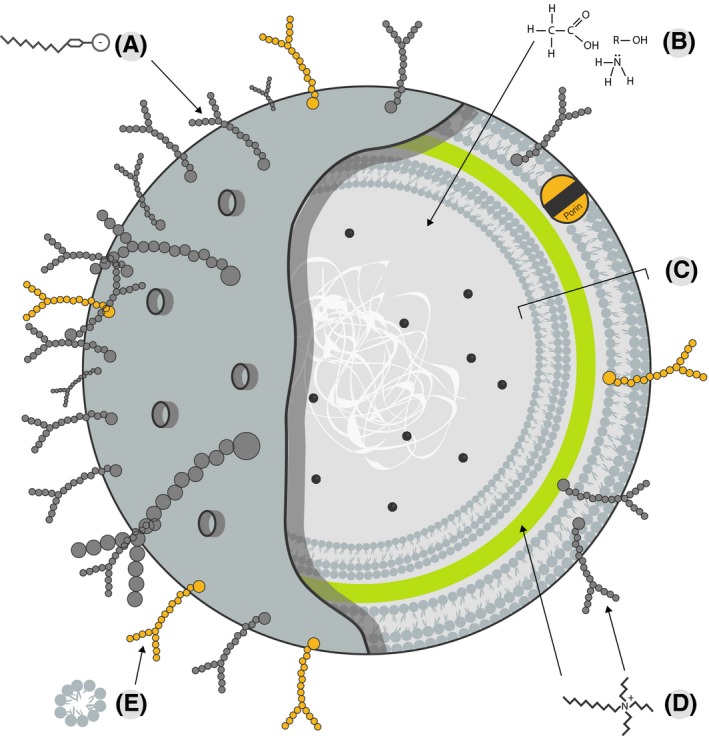
Chemical‐based cleaning acts on various cellular components which may be specific to a particular domain or cell type or generalizable across many types. (A) Anionic detergents disrupt lipopolysaccharides in the cell membrane of Gram‐negative bacteria. (B) Vinegars, ammonia, and alcohols disrupt the osmolarity of a cell. (c) The cell wall of a Gram‐negative bacterium is complex, including outer cell membrane, periplasmic space, peptidoglycan, and inner cell membrane. (D) Cationic detergents disrupt the normal activities of peptidoglycan in cell walls and lipopolysaccharides in cell membranes. (E) Detergents (eg, sodium laureth sulfate) disrupt the attachment of cells to surfaces and disrupt lipid membranes through hydrophobic interactions with glycopolysaccharides
