Figure 1.
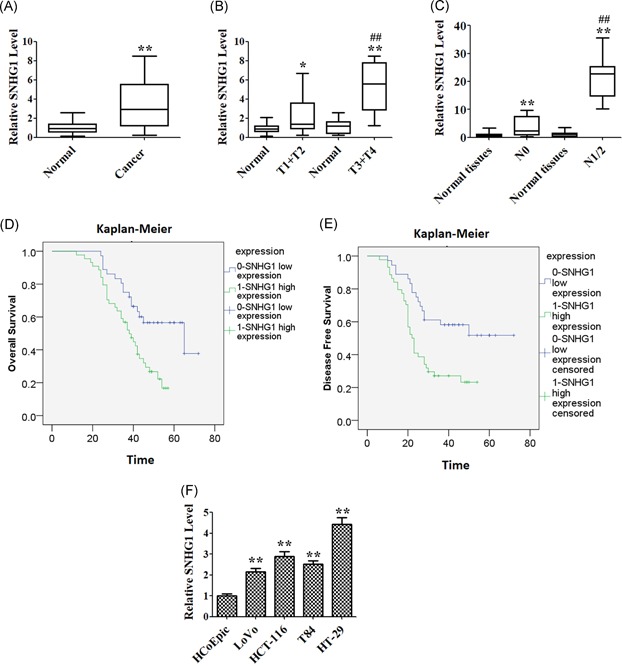
Clinical significance of SNHG1 level in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells. (A) The level of SNHG1 was detected using quantitative real‐time polymerase chain reaction (qRT‐PCR) assay in CRC tissues and normal tissues (n = 40). (B) qRT‐PCR assay was used to detect the level of SNHG1 in tumor tissues of different TNM stages (T1 + T2 or T3 + T4) and normal tissues, respectively. (C) QRT‐PCR assay was used to detect the level of SNHG1 in tumor tissues from patients with (N1 + N2) or without (N0) lymphatic metastasis, respectively. (D) Kaplan‐Meier analysis revealed that high expression of SNHG1 was related to the poor overall survival of CRC patients. (E) Kaplan‐Meier analysis revealed that high expression of SNHG1 was related to poor disease‐free survival of CRC patients. (F) The expression of SNHG1 in four CRC cell lines (LoVo, HT‐29, T84, HCT116) and a nontumor colorectal epithelial line (HCoEpic) were detected using qRT‐PCR assay. Data represent mean ± SD, n = 3; *P < .05, **P < .01 compared with the normal or HCpEpic group; ## P < .01 compared with T1 + T2 or N0 group [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
