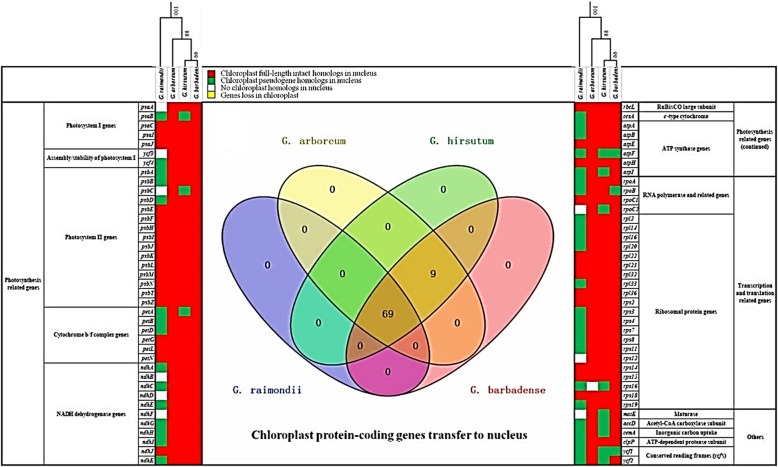
Fig. 5.
Chloroplast genes transfers to the nuclear genome in four cotton species. The columns on the left and right represent the functional categories and names of chloroplast-encoded genes. The first line lists the names of plant species and the phylogenetic relationship above. The red and green cells represent chloroplast full-length intact homologs and pseudogenes in nuclear genomes, respectively. White and yellow cells represent no chloroplast homologs in nuclear genomes and genes lost from chloroplast genomes, respectively. Center: Venn diagram containing all chloroplast protein-coding genes transferred into the nuclear genome (corresponding to the red and green cells) in G. arboreum (yellow), G. raimondii (blue), G. hirsutum (green), and G. barbadense (red). The overlap among circles shows the common nupts among those species