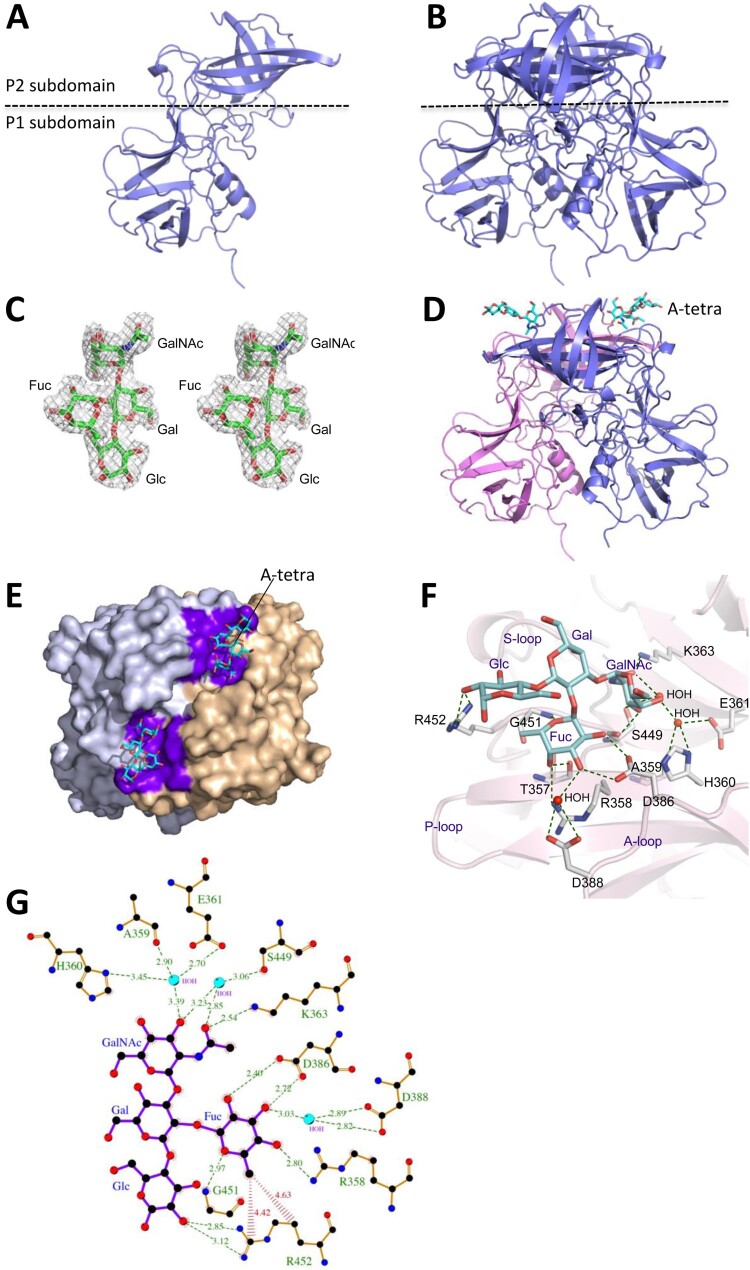
Figure 3.
The crystal structures of the GII.3 TV24 P proteins and the HBGA binding site (HBS). (A and B) Structure of the native TV24 P protein monomer (A) and dimer (B) in the ribbon model at the side view. The dashed line shows the boundary between the P2 and the P1 subdomains. (C) Stereo view of (mFo-DFc) electron density map contoured at 2.0σ (grey) of the type A tetrasaccharides (A-tetra) that were calculated from diffraction intensity of complex data with the phase angle of native protein structure. (D) Side view of the P dimer-A-tetra complex. Structures of the two TV24 P proteins (ribbon model) are in magenta and blue, respectively, with indicated A-tetra (stick model) on the top. (E) Top view of the P dimer-A-tetra complex, showing the HBSs. The two P monomers (surface model) are in grey and light orange, respectively. The residues forming the HBSs are shown in purple, while the bound A-tetras (stick model) are in cyan. (F) The interaction networks between the TV24 HBS and the A-tetra. The amino acids that form the HBS are shown with labels in stick model in grey, while the A-tetra with indications of the N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), fucose (Fuc), galactose (Gal), and glucose (Glc) is shown in cyan (stick model). The hydrogen bonds are shown by blue dashed lines. The A-, S- and P-loops are also indicated. (G) Ligplot of the detailed hydrogen bond (green dashed lines) and hydrophobic interactions (red lines) network between amino acids (orange) of the HBS and individual saccharides of the A-tetra (purple). Non-ligand residues located around A-tetra that do not participate in direct hydrogen bonding are shown as red shining partial circles. Water molecules are shown in cyan, carbon atoms in black, oxygen atoms in red, nitrogen atoms in blue.