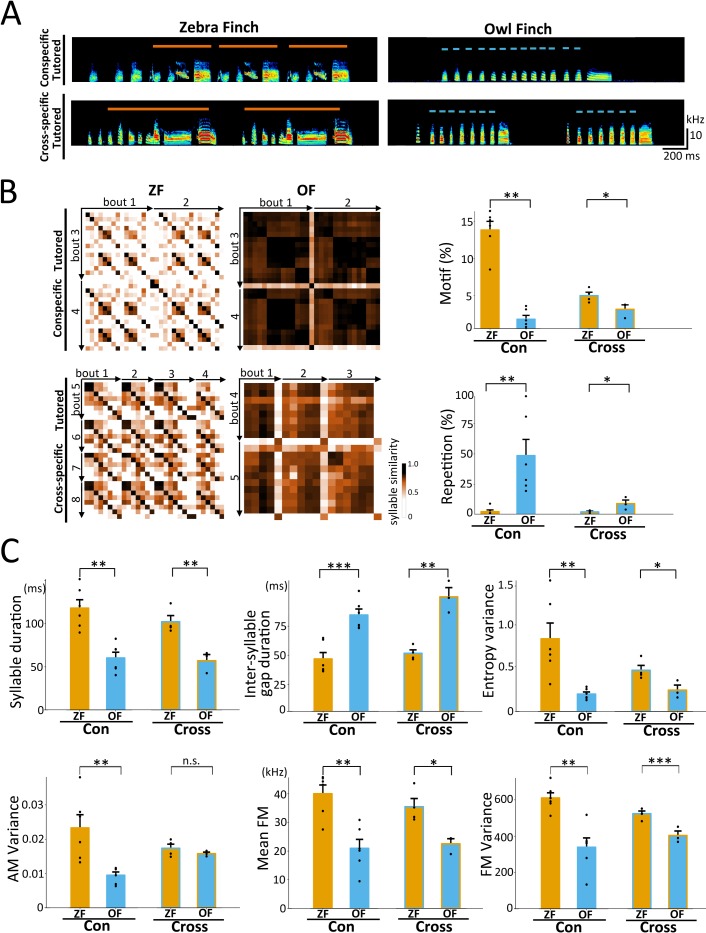
Fig 2. Species difference in song structures between ZF and OF.
(A) Typical examples of songs from ZFs and OFs that were reared with conspecific song tutoring and cross-species song tutoring. Orange solid and blue dotted lines represent the motif and repetitive structure of syllables, respectively. (B) Species differences in the syllable sequence of ZF and OF songs. (Left) Syllable similarity matrices for songs produced by ZFs and OFs that were reared with conspecific song tutoring and cross-species song tutoring. (Right) Motif and repetition indices of ZF and OF songs (n = 6 each from conspecific song tutored ZF and OF, n = 4 and 3 from cross-species song tutored ZF and OF, respectively; one-way ANOVA, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). Each dot corresponds to an individual bird. (C) Species differences in syllable acoustics (syllable duration, inter-syllable gap duration, entropy variance, AM variance, mean FM, and FM variance) of ZF and OF songs (“Con”: n = 6 each from conspecific song tutored ZF and OF; “Cross”: n = 4 and 3 from cross-species song–tutored ZF and OF, respectively; one-way ANOVA, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). Each dot corresponds to an individual bird. Relevant data values are included in S1 Data. AM, amplitude modulation; FM, frequency modulation; OF, owl finch; ZF, zebra finch.