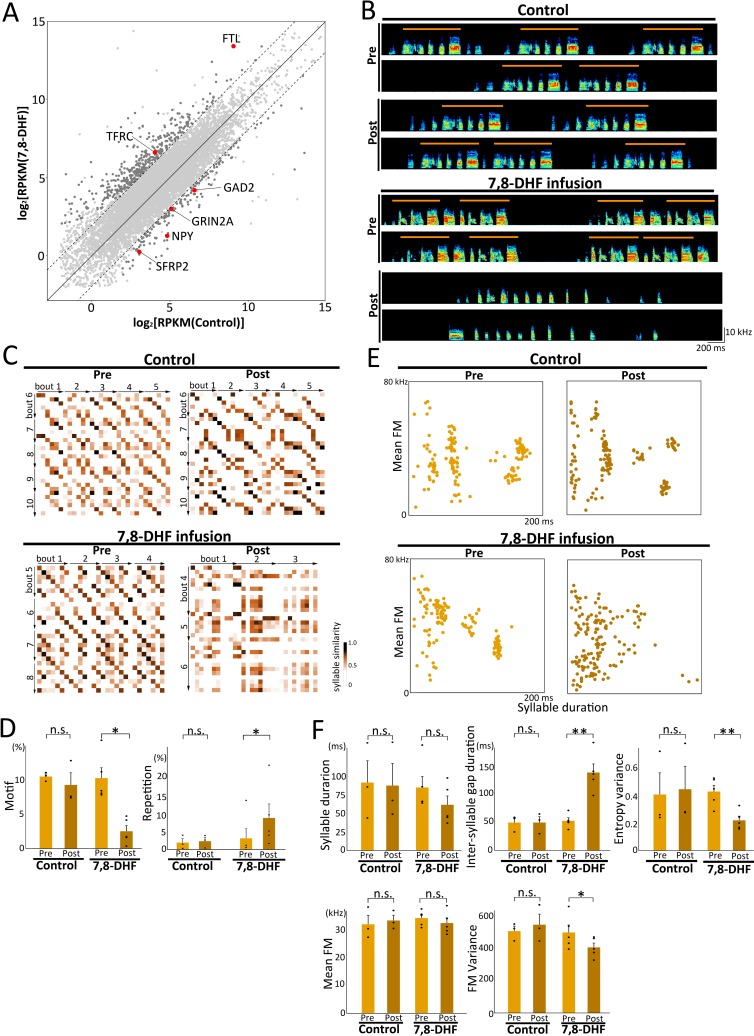
Fig 7. Obliteration of species specificity of ZF song by BDNF receptor agonist infusion into RA.
(A) Scatterplot indicating RA gene expression in control and 7,8-DHF–infused birds. Dashed lines represent the boundary of the 4-fold expression difference. Darker gray colored dots represent significant differences in expressed genes higher than 4-fold between the control and 7,8-DHF–infused birds. Red colored dots represent downstream trans-regulated genes of BDNF (represented in Fig 5C). (B) Songs before and after infusing BDNF receptor TrkB agonist, 7,8-DHF. Typical examples of songs from control and 7,8-DHF–infused birds. Orange solid lines represent the motif structure of ZF songs. (C) Examples of syllable sequence changes between pre- and post-infusion. Syllable similarity matrices for a pair of songs produced by control and 7,8-DHF–infused birds. (D) Changes in the frequency of motif and repetition in songs at pre- and post-infusion stages (control ZF, n = 3, ZF with 7,8-DHF infusion [7–10 days], n = 5; paired t test, *p < 0.05). Each dot corresponds to individual birds. (E) Examples of syllable acoustic changes between pre- and post-infusion. Scatterplots indicate the distribution of 150 syllables (duration versus mean frequency) from control and 7,8-DHF–infused birds. (F) Changes in syllable acoustics (syllable duration, inter-syllable gap duration, entropy variance, mean FM, and FM variance) of songs at pre- and post-infusion stages (control ZF, n = 3, ZF with 7,8-DFH infusion [7–10 days], n = 5; paired t test, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, n.s., not significant). Each dot corresponds to an individual bird. Relevant data values are included in S6 Data. BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; FM, frequency modulation; RA, robust nucleus of the arcopallium; RPKM, reads per kilobase of transcript per million reads mapped; TrkB, tropomyosin receptor kinase B; ZF, zebra finch; 7,8-DHF, 7,8-dihydroxyflavone.