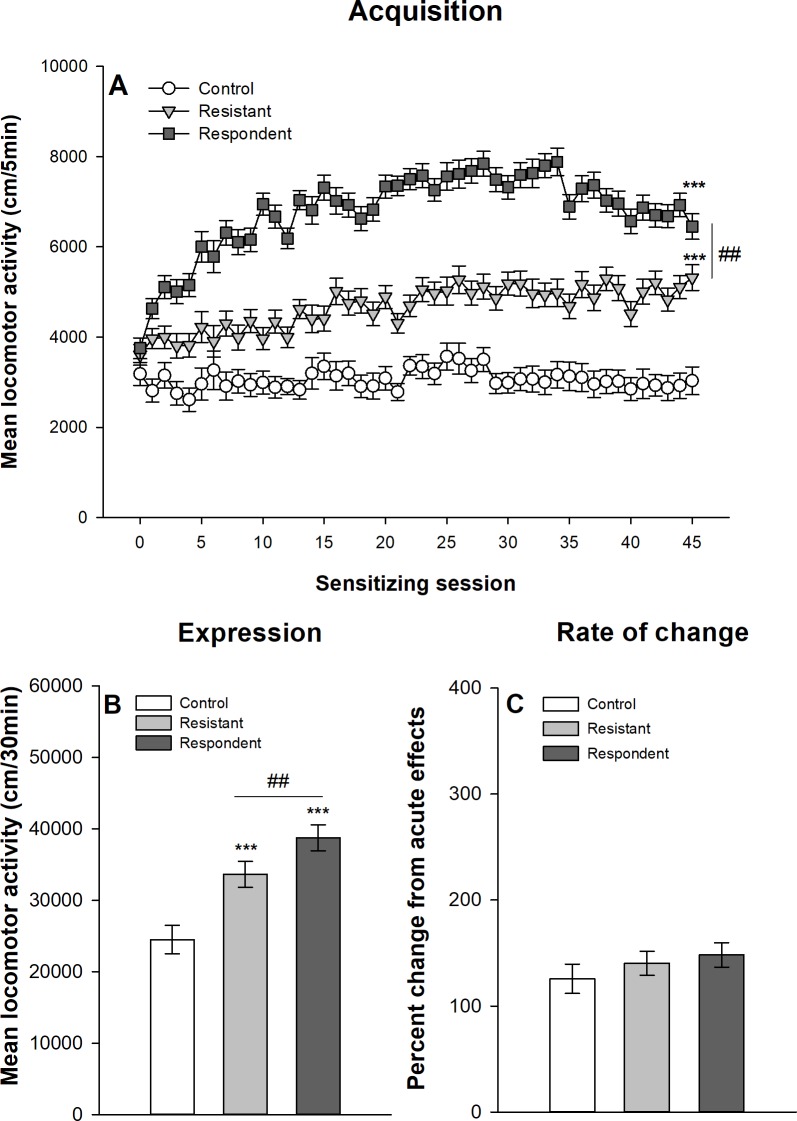
Fig 10. Acquisition and expression of behavioral sensitization following 45 ethanol administrations in female DBA/2J mice classified according to the extreme group procedure.
Mice sensitized to ethanol were split according to their locomotor activity during the 21th ethanol session following an extreme group approach. The upper 30% of the distribution was classified as “respondent” and the lower 30% as “resistant” according to Souza-Formigoni et al. [14–16,27–29,31–35,37–40]. The remaining 40% of sensitized mice was not included in the figure and in the analysis. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. (A) shows the acquisition of behavioral sensitization in mice daily injected with ethanol (respondent and resistant) or saline (control). ***p<0.0001: significantly different from the first acquisition session. ###p<0.0001: significant difference between resistant and respondent groups of mice on the 45th ethanol session. (B) depicts the total distance travelled during the test of sensitization following an ethanol injection for the three groups. ***p<0.0001: significantly different from the control group that was repeatedly injected with saline during the acquisition sessions. ##p<0.01: significant difference between resistant and respondent groups of mice. (C) represents the percentage of change in locomotor activity between the first and the last ethanol sessions (D45/D1) for each group.