Fig. 3. The ELeCt platform enables enhanced and targeted delivery of NP drugs to the lungs bearing metastasis.
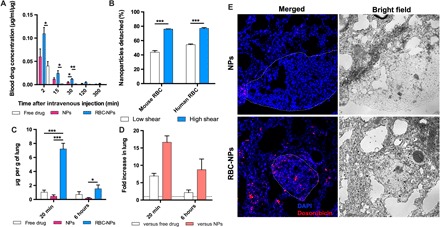
(A) Pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered DOX formulations. Extended blood circulation time of DOX was achieved by erythrocyte hitchhiking compared with using free drug or NPs alone (n = 3). Significantly different [one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA)]: *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. (B) Hitchhiked drug-loaded NPs could specifically detach from mouse and human erythrocytes under the lung-corresponding shear stress. Samples were sheared for 20 min (n = 3). Low shear indicates rotary shear (~1 Pa), while high shear was at 6 Pa. Significantly different (Student’s t test): ***P < 0.001. (C) Drug accumulation in the lungs of mice bearing B16F10-Luc lung metastasis at 20 min and 6 hours after intravenous administration of different DOX formulations (n = 3). Significantly different (one-way ANOVA): *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001. (D) Comparison of the drug concentration in the lungs of erythrocyte hitchhiking group to that of the free drug and NP-alone groups (n = 3). (E) Drug distribution in the diseased lungs 20 min after intravenous administration of DOX formulations. Dashed lines indicate the edge of metastasis nodules.
