Fig. 6. RvDp5 and sFgl2 synergistically accelerate sepsis catabasis.
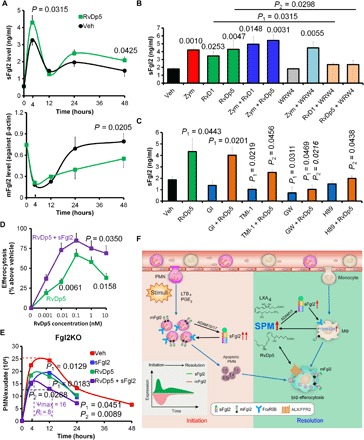
(A) WT C57BL/6 mice were injected intraperitoneally with Zym (1 mg) using PBS or RvDp5 (200 ng), and exudate sFgl2 and peritoneal leukocytic mFgl2 were assessed. (B) Murine MΦs were treated with Zym (100 ng/ml), RvD1 (10 nM), RvDp5 (10 nM), and WRW4 (1 μM) as indicated. The supernatant expression of sFgl2 was detected with ELISA. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. Numbers upon the groups were P values as compared with vehicle. P1 represents the comparison between RvD1 and RvD1 + WRW4, while P2 represents the comparison between RvDp5 and RvDp5 + WRW4. (C) After human MΦs were treated with PBS (Veh), RvDp5 (10 nM) with or without GI254023X (10 μM), TMI-1 (10 μM), GW280264X (10 μM), or H89 (10 μM) for 24 hours, sFgl2 in the supernatant was assessed with ELISA. (D) WT C57BL/6 murine MΦs were treated with RvDp5 (0 to 10 nM) with or without sFgl2 (10 μg/ml) for 1 hour and then coincubated with CFDA-labeled apoptotic PMNs (1:3) for another 1 hour. The percent increases of efferocytosis are shown. (E) Fgl2KO mice were injected intraperitoneally with Zym (1 mg) using PBS, RvDp5 (200 ng), and/or sFgl2 (200 ng). The exudate PMNs were enumerated. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. P1 represents value compared with vehicle; P2 represents value compared with RvDp5 alone. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. (F) Schematic mechanism of Fgl2 and RvDp5 programming inflammation resolution. Inflammatory stimuli trigger the infiltration of PMN and ADAM10/17-mediated Fgl2 shedding. By binding to FcγRIIB, sFgl2 promotes the apoptosis of PMN, which recruit monocytes and MΦs for efferocytosis. The exudate sFgl2 enhances the expression of 12/15-LOX in MΦs and the production of SPM, including RvDp5 and LXA4. RvDp5 and LXA4 activate ALX/FPR2 to promote ADAM17-mediated sFgl2 shedding, thereby synergistically facilitating inflammation resolution.
