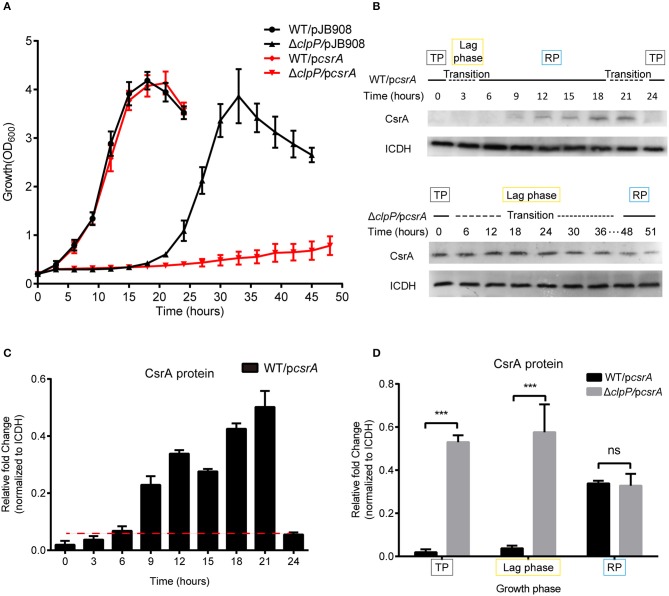
Figure 2.
Accumulation of CsrA due to loss of ClpP regulation delays the transition of L. pneumophila from the TP into the RP. (A) Growth curves of L. pneumophila wild-type strain WT (•), the clpP deletion mutant ΔclpP (▴), WT with csrA expression (WT/pcsrA) (), ΔclpP with csrA expression (ΔclpP/pcsrA) (). For negative controls, pJB908 vector was electroporated into WT and ΔclpP to create WT/pJB908, ΔclpP/pJB908, respectively. Bacterial strains in TP (OD600 = 3.0–3.5) were grown in AYE medium at 37°C and samples were taken every 3 h for determination of optical density at 600 nm. (B) Ectopic protein levels of CsrA during the bacterial growth period. Bacterial whole-cell lysates from WT/pcsrA and ΔclpP/pcsrA were prepared and an immunoblot of CsrA was probed with an anti-His tag antibody. ICDH was measured as a loading control. RP refers to the exponential growth of bacteria in AYE broth, and TP refers to the period approximately 6 h after the cessation of growth. Lag phase refers to the transition from transmissive phase to replicative phase in rich medium. (C) Ectopic protein levels of CsrA in WT/pcsrA calculated by ImageJ at the indicated time points. (D) Relative protein levels of CsrA in the RP, lag phase, and TP of WT/pcsrA and ΔclpP/pcsrA calculated by ImageJ. Bacterial cells in the RP were harvested at an OD600 of 0.7–1.0 and those in the TP were harvested approximately 6 h after the cessation of growth. Data represent mean ± SD derived from three independent experiments. ***p < 0.001 were identified by GraphPad Prism.