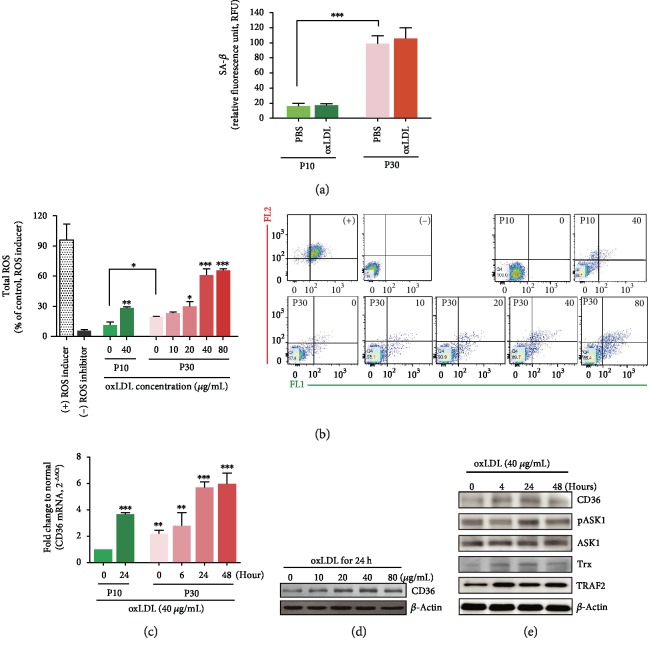
Figure 1.
oxLDL induces ROS overexpression and intracellular signals in senescent human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs). (a) SA-β-Gal activities in passage 10 (P10) and passage 30 (P30) of HAECs were assayed with or without oxLDL (40 μg/mL) for 24 hours. (b) Total intracellular ROS amounts increased in an oxLDL dose-dependent manner up to a concentration of 40 μg/mL and increased more in senescent HAECs compared to young cells. (c) Stimulation with oxLDL (40 μg/mL) increased the CD36 mRNA level in a time-dependent manner. Each level is shown as the relative fold changes compared to normal young HAECs. (d) The CD36 protein expression rose when HAECs were exposed to oxLDL. (e) The protein expressions of CD36, pASK1, ASK1, Trx, and TRAF2 were analyzed via a time-dependent Western blot at 40 μg/mL oxLDL. The ROS inducer-treated group was presented as a positive control, and the ROS inhibitor-treated group was shown as a negative control. Results are expressed by mean and standard deviation. Significance is presented as follows: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001.