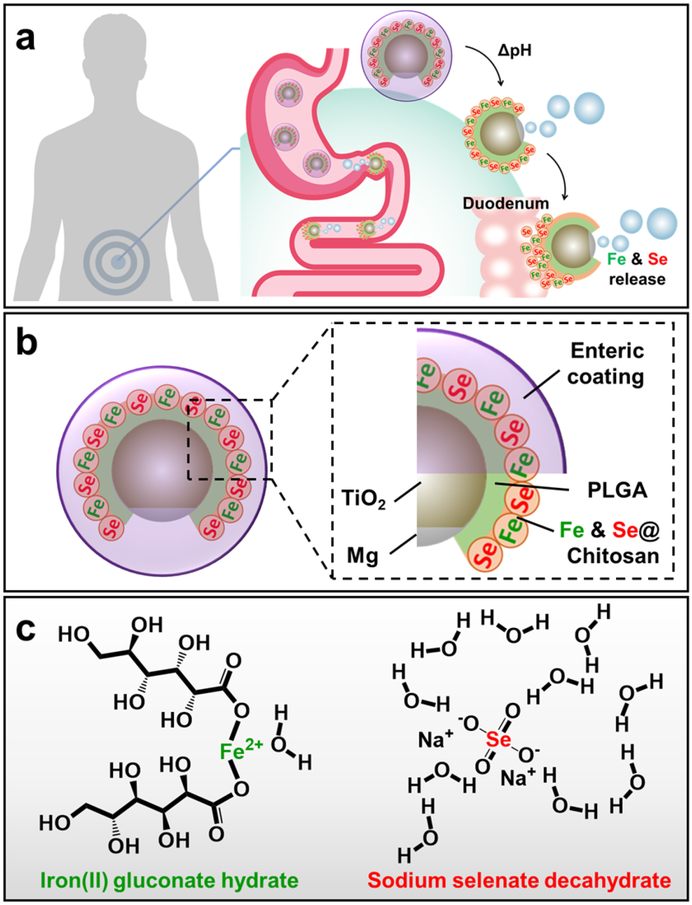
Figure 1.
Schematic illustrations of synthetic micromotors for active delivery of minerals. a, Schematic of micromotor-based in vivo delivery and release of Fe and Se at the duodenum region. b, Schematic structure of the mineral-loaded micromotor consisting of a Mg/TiO2 core protected with an inner PLGA polymer layer, a middle chitosan layer loaded with Fe and Se, and an outer pH-responsive enteric layer (Eudragit® L100–55, soluble when pH ≥ 5.5). c, Chemical structures of iron(II) gluconate hydrate (left) and sodium selenate decahydrate (right).