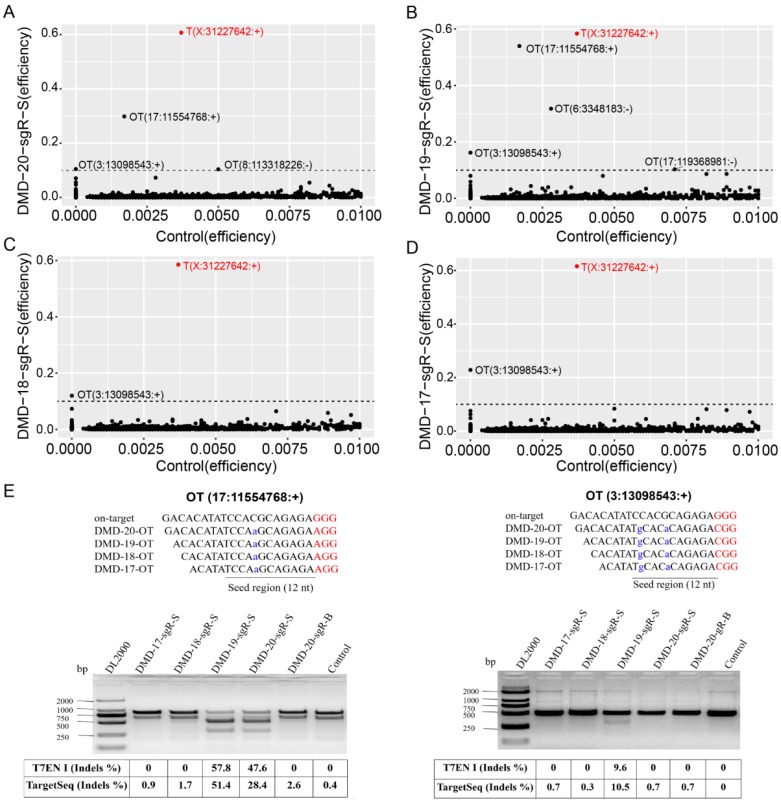
Figure 4.
Detection of on- and off-target site cleavage activities in different lengths of sgRNAs but targeting DMD gene based on in silico prediction and Target capture sequencing. (A), (B), (C), and (D) are the results of the on- and off-target cleavage efficiencies of 20, 19, 18, and 17 nt sgRNAs by Target capture sequencing in the sorted cell population, respectively. T (X:31227642:+) represents the on-target site, while OT for off-target site of sgRNA. The x- and y-axis represent the Indel efficiencies of on- and off-targets for sgRNAs in the control and gene-editing groups, respectively. The number of reads ≧ 10 is the threshold of control group representing the captured target, and the Indel efficiency is ≦ 1 %. (E) Validation of off-target sites for 20, 19, 18, and 17 nt sgRNAs using T7ENI cleavage assay. The Indel efficiency below the agarose gel electrophoresis shows the detection of the same predicted off-target site by the T7ENI cleavage assay and TargetSeq. Seed region represents seed sequences, which are the first 1-12 positions of the spacer immediately in the 5′ end to the PAM sequence. Control represents the negative control group; DL2000: DNA ladder; Nucleotides marked in red and blue colors represent protospacer adjacent motif (PAM), and mismatches and OT for off-target, respectively, OT: predicted off-target site.