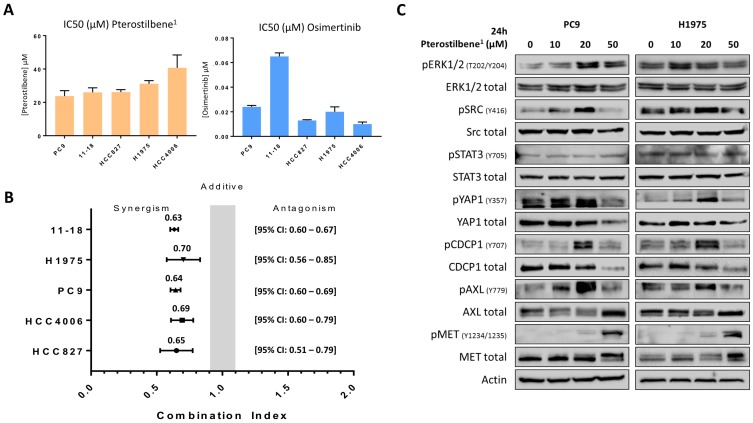
Figure 2.
The effects of single and combined osimertinib and pterostilbene1 treatment. A: MTT cell viability assays were performed in 5 different EGFR-mutation positive NSCLC cell lines (PC9, H1975, 11-18, HCC4006 and HCC827), to determine the effects of pterostilbene1 on cell viability, and to determine the IC50 in each cell line. Results of previously performed experiments with osimertinib in the same cell lines are also shown. Experiments were performed in biological triplicates, and the average and standard deviations are shown. B: In all cell lines MTT cell viability assays were performed to explore the effect of combined osimertinib and pterostilbene1 treatment. Combination indexes were calculated based on the Chou and Talalay method, and values <1, =1 and >1 indicate synergism, additive effect and antagonism, respectively. Experiments were performed in biological triplicates, and the averages and 95% CIs are shown. C: PC9 and H1975 cells were treated with different concentrations of pterostilbene1 for 24 h. Untreated cells received an equivalent dose of vehicle (DMSO). Cell lysates were used for immunoblotting, and the effect of pterostilbene1 treatment on downstream components was explored. Experiments were performed in biological triplicates with similar results, and a representative blot is shown. DMSO: dimethylsulfoxide; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; IC50: the half maximal inhibitory concentration; MTT: 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide; NSCLC: non-small cell lung cancer; 95%CI: 95% confidence interval.