Figure 1.
Analysis of LN01 mAb Sequence and Neutralization
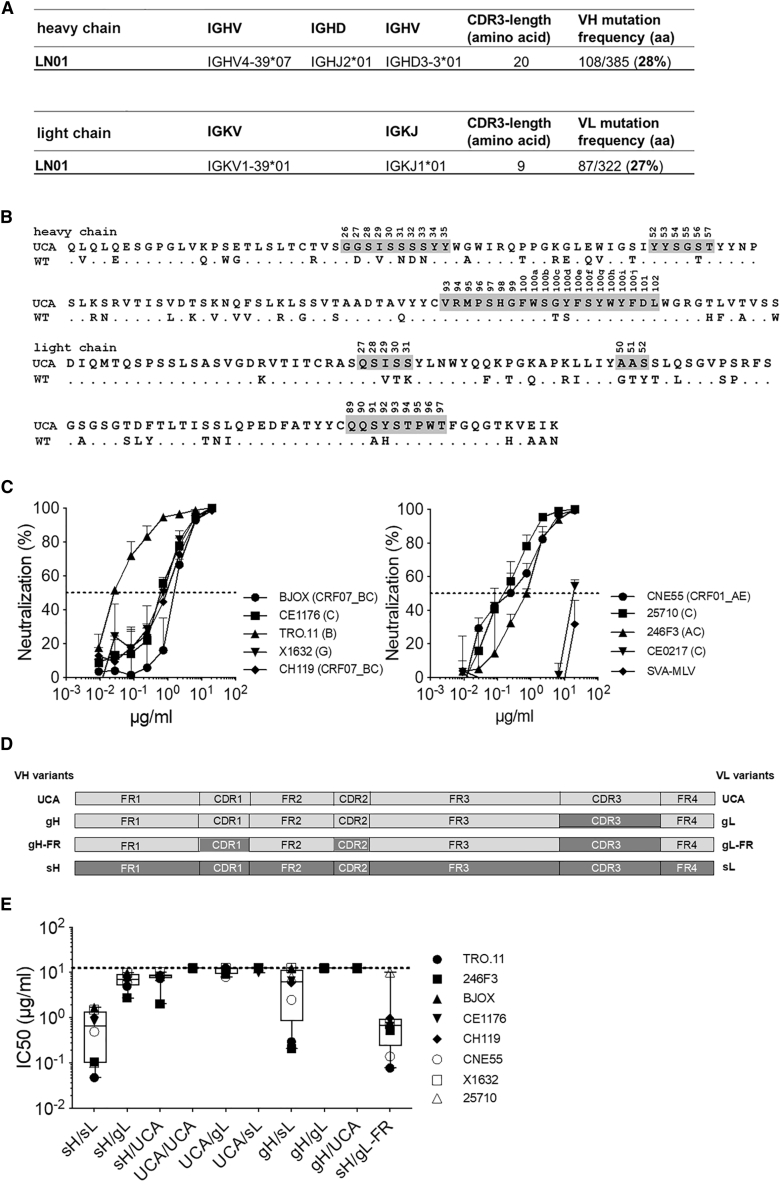
(A) Analysis of LN01 sequences showing the inferred germline genes and alleles encoding the variable region of the heavy and light chains, the amino acid length of the CDR3 regions and the mutation frequency of the variable regions of the light and heavy chains (aa, amino acid).
(B) Alignment of the amino acid sequences of the variable regions of LN01 wild-type and LN01 UCA. The CDRs regions are highlighted in gray.
(C) LN01 IgG1 activity was tested in vitro in neutralization assay using TZM-bl cells. Different concentrations of the antibody were tested against nine pseudoviruses (PVs) of the Global Panel plus a control PV (SVA-MLV). Shown on y axes is the % of neutralization and the standard deviation (SD) calculated on quadruplicates.
(D) Schematic of LN01 unmutated common ancestor (UCA) and variants created for investigation of the neutralization requirements of LN01 germlined variants. Light gray areas represent sequence from UCA; dark gray regions are from the somatic, mature antibody. Wild-type, somatically mutated heavy (sH), or somatically mutated light (sL) chains; gH or gL, germline V-gene revertants of sH or sL in which HCDR3 or LCDR3 are mature; gH-FR or gL-FR, germline V-gene revertants of sH or sL in which HCDRs or LCDRs are mature.
(E) Box-and-whisker plots showing the neutralizing activity of LN01 germline variants against a panel of eight PVs of the Global Panel as measured using a neutralization assay on TZM-bl cells.