FIG 2.
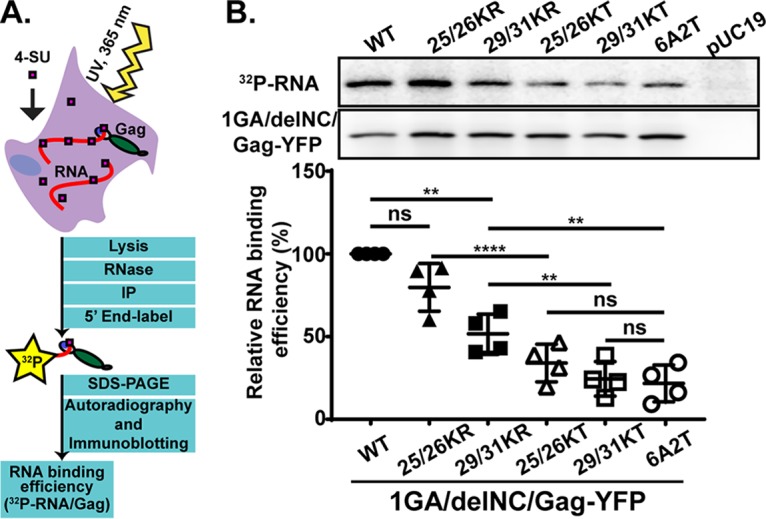
Gag derivatives with KR mutations in the MA-HBR bind RNA efficiently compared to those with KT mutations. (A) Schematic illustration of the PAR-CLIP assay. A cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter-driven Gag-YFP construct lacking the myristoylation site (1GA) and most of the NC domain (delNC) was used as the backbone for the Gag derivatives analyzed in this assay. A mutant Gag with all MA-HBR basic residues switched to neutral Ala or Thr, 6A2T, was used as a negative control. To identify bands representing Gag, a non-Gag plasmid, pUC19, was used as an additional control. The 1GA/delNC/Gag-YFP constructs were expressed in HeLa cells and cross-linked to 4-SU-containing RNA in the cells. Gag proteins were recovered by immunoprecipitation (IP), Gag-bound RNA was end labeled with 32P, and signals for Gag proteins and Gag-bound RNA were detected by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting and autoradiography, respectively. (B, top) Representative results for 32P-labeled Gag-bound RNA detected by autoradiography and total Gag detected by immunoblotting and chemiluminescence. (Bottom) Relative RNA binding efficiency (percent) of MA-HBR mutants determined by quantifying the intensity of RNA signals normalized by the Gag band intensity on the same PVDF membrane. Results from 4 independent experiments are shown as means ± standard deviations. P values were determined using Student’s t test, using raw data. ns, not significant; **, P ≤ 0.01; ****, P ≤ 0.0001.
