FIG 6.
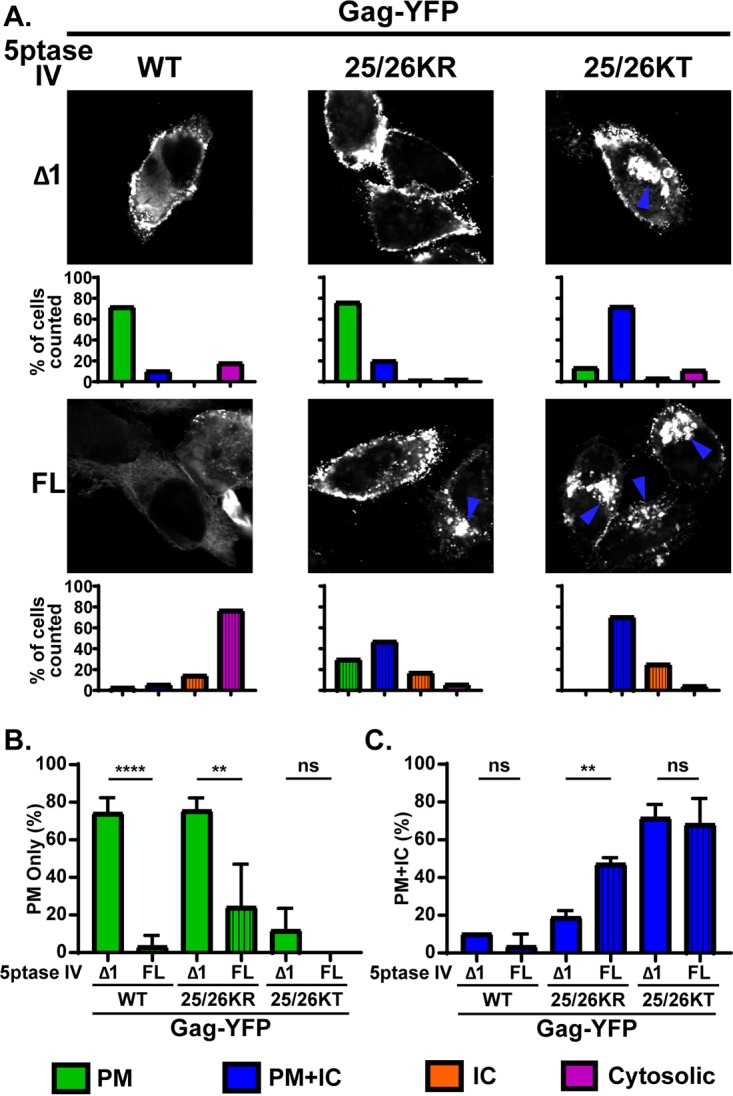
Depletion of cellular PI(4,5)P2 leads to promiscuous subcellular localization of 25/26KR Gag-YFP. (A) HeLa cells were transfected with WT Gag-YFP, 25/26KR Gag-YFP, or 25/26KT Gag-YFP along with myc-tagged FL 5ptaseIV or the catalytically inactive Δ1 derivative. At 14 h posttransfection, cells were stained with ConA-AF594 (not shown), fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS, permeabilized, immunostained with mouse monoclonal anti-myc antibody and anti-mouse IgG conjugated with Alexa Fluor 405 (not shown), and analyzed using a fluorescence microscope. Only cells positive for both myc-tagged 5ptaseIV and Gag-YFP were included in the analysis. Sixty-nine to 134 cells were analyzed under each condition across 3 independent experiments. Representative confocal images of Gag-YFP are shown. The blue arrowhead indicates the Gag-YFP signal in the intracellular compartments. The localization patterns were examined as described in the legend of in Fig. 3, and the percentages of total cells showing the indicated subcellular distribution patterns under each condition are shown in bar graphs. (B and C) Percentages of cells showing a PM-only distribution of Gag-YFP (B) and PM and intracellular compartment distribution of Gag-YFP (C) compared between cells expressing FL and Δ1 5ptaseIV across 3 independent experiments. Data are presented as means ± standard deviations. P values were determined by Student’s t test. ns, not significant; **, P ≤ 0.01; ****, P ≤ 0.0001.
