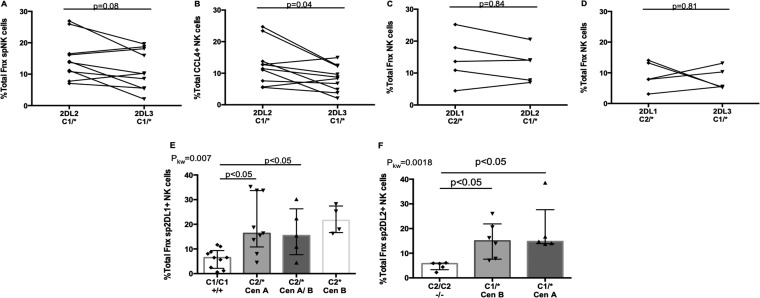
FIG 4.
Comparison of the responses to autologous iCD4 cells of spKIR2DL1+, spKIR2DL2+, and spKIR2DL3+ NK cells from the same donor and the influence of their allotypes on responses to iCD4 cells. (A to D) The y axes show the frequencies of functional cells characterized by the sum of all functions (A, C, and D) or CCL4 secretion (B) for 10 pairs of educated spKIR2DL2+ and spKIR2DL3+ NK cells (A and B), 5 pairs of educated spKIR2DL1+ and spKIR2DL2+ NK cells (C), and 5 pairs of educated spKIR2DL1+ and spKIR2DL3+ NK cells (D) from the same donors. The significance of within-individual differences was assessed using Wilcoxon matched pairs tests. (E) Frequencies of iCD4 cell-stimulated functional spKIR2DL1+ NK cells generated by donors cocarrying a noneducating C1/C1 genotype or educating C2/* genotypes. The frequency of functional cells was compared for donors cocarrying C2/* with KIR2DL1 genotypes where both alleles mapped to the centromeric KIR haplotype A (Cen A), one allele mapped to Cen A and the other to the centromeric KIR haplotype B (Cen B), or both alleles mapped to Cen B. (F) Frequencies of iCD4 cell-stimulated functional spKIR2DL2+ NK cells generated when donors cocarried a noneducating C2/C2 genotype or an educating C1/* genotype. The frequency of functional cells was compared for donors cocarrying C2/* with KIR2DL2 genotypes where both alleles mapped to Cen A or Cen B. Each point represents results for a single individual. For each data set, the bar height and error bars show the median and interquartile range, respectively. P values are given above the bars linking the data sets being compared. 2DL1, spKIR2DL1+; 2DL2, spKIR2DL2+; 2DL3, spKIR2DL3+; C1/*, either C1/C1 or C1/C2; C2/*, either C1/C2 or C2/C2.