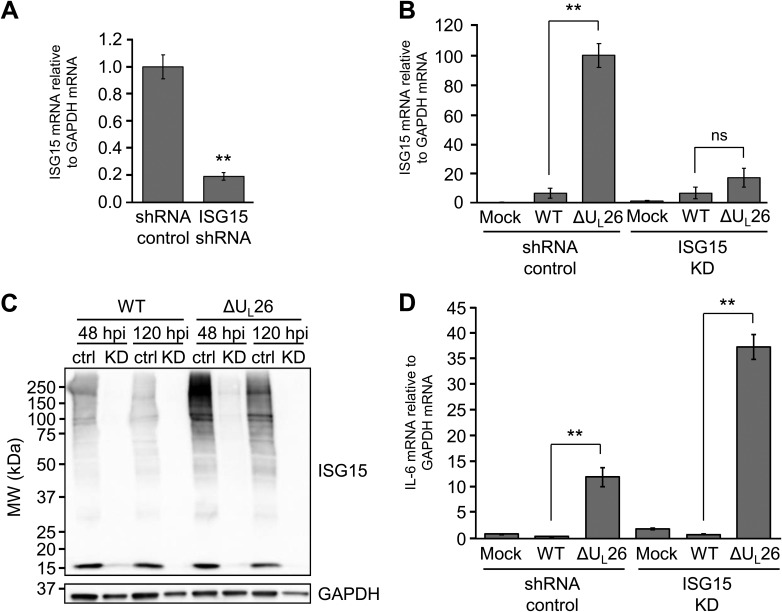
FIG 3.
The ΔUL26 mutant-mediated induction of ISG15 transcription is required for the enhancement of protein ISGylation but is dispensable for the induction of IL-6 expression during ΔUL26 mutant infection. (A) HFF cells were transduced with either a control shRNA construct or a construct encoding an ISG15-targeting shRNA. The abundance of ISG15 transcript was measured by real-time PCR and normalized to GAPDH. Values are means ± SEM (n = 5; **, P < 0.01). (B) HFF shRNA control and ISG15 KD shRNA-transduced cells were either mock infected or infected with WT or ΔUL26 mutant HCMV at an MOI of 3.0. Cellular RNA was harvested at 48 hpi, and ISG15 mRNA abundance was assessed by real-time PCR and normalized to GAPDH. Values are means ± SEM (n = 5; **, P < 0.01; ns, not significant). (C) HFF shRNA control (ctrl) and ISG15-targeting shRNA-transduced (KD) cells were infected as in panel B. Cellular protein was harvested at the indicated time points and Western blotted with antibodies directed at ISG15 and GAPDH. (D) HFF shRNA control and ISG15 KD cells were infected as in panel B, RNA was harvested at 48 hpi, and IL-6 mRNA abundance was assessed by real-time PCR and normalized to GAPDH. Values are means ± SEM (n = 5; **, P < 0.01).