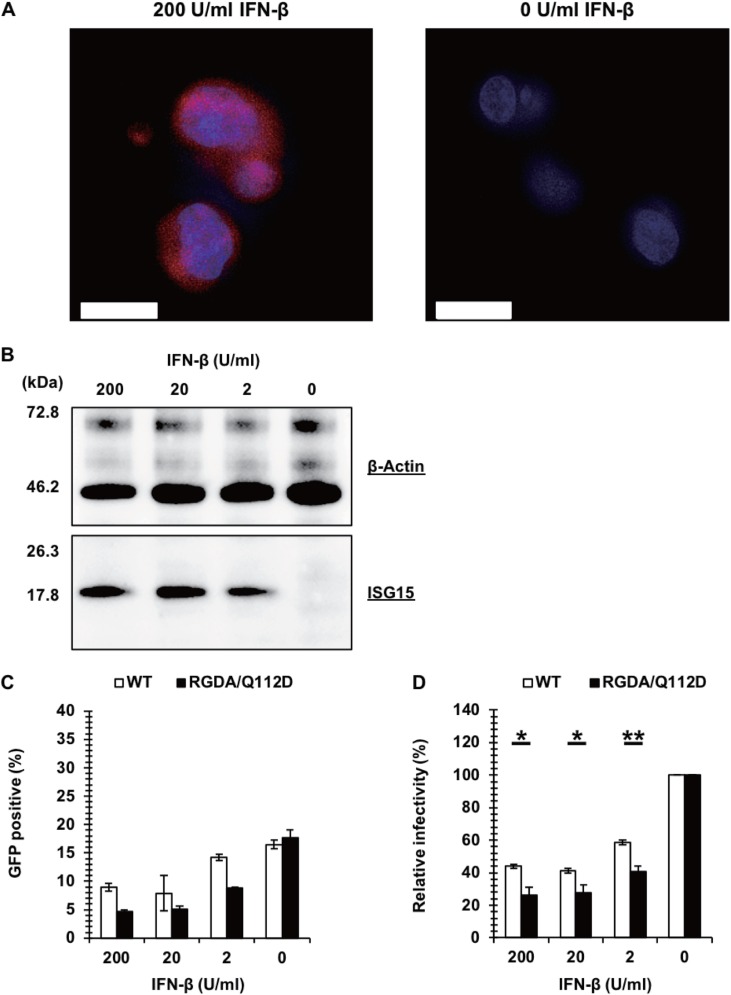
FIG 1.
A cyclophilin A binding-deficient capsid mutant, the RGDA/Q112D virus, is hypersensitive to IFN-β in T cells. (A) Jurkat cells treated with 200 U per ml of IFN-β or left untreated were examined for the induction of ISG15 (red, ISG15 monoclonal antibody; blue, Hoechst dye). Bars, 10 μm. (B) Expression level of ISG15 in Jurkat cells treated with 200, 20, 2, or 0 U per ml of IFN-β. Western blots of cell lysates extracted from Jurkat cells were probed with an anti-ISG15 antibody (bottom) or an anti-β-actin antibody (top). The positions of the molecular weight markers are shown on the left side. (C) Jurkat cells treated with 200 U, 20 U, 2 U, or 0 U per ml of IFN-β were infected with VSV-G-pseudotyped GFP reporter viruses. The level of GFP expression was determined at 2 days after infection. One representative result of at least three independent experiments is shown, with error bars denoting the standard deviation (SD) of the mean of triplicate measurements. (D) The relative IFN-β sensitivity (compared with that for untreated cells [in percent]) was calculated by dividing the percentage of GFP-positive cells among IFN-β-treated cells by that among untreated cells. The mean from three independent experiments is shown, with error bars denoting the standard error of the mean (SEM). **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05.