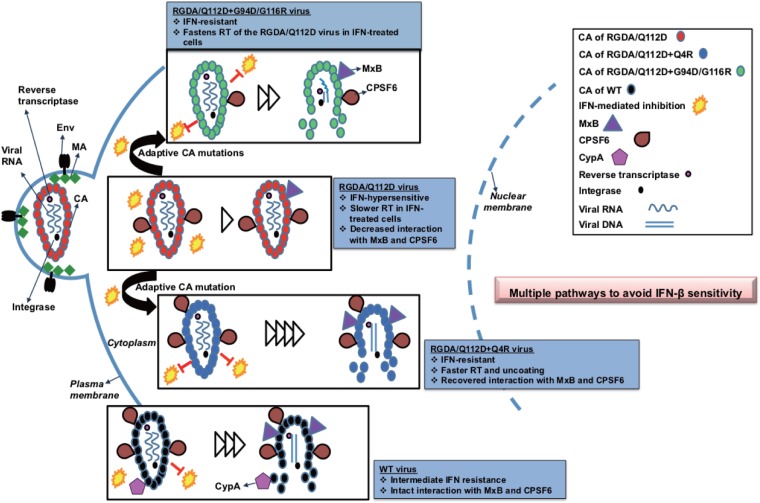
FIG 11.
Multiple pathways to avoid IFN sensitivity of HIV-1 by mutations in the capsid. An IFN-hypersensitive CA mutant RGDA/Q112D virus (red) evolved to be IFN resistant by acquiring additional Q4R or G94D/G116R mutations. The IFN-resistant RGDA/Q112D+Q4R virus (blue) shows accelerated kinetics of reverse transcription (RT) and a faster initiation of uncoating in both the presence and the absence of IFN. The virus shows recovered interactions with MxB and CPSF6. Another IFN-resistant virus, the RGDA/Q112D+G94D/G116R virus (green), accelerates the kinetics of reverse transcription to a smaller degree only in the presence of IFN. The virus showed a degree of interaction with MxB similar to that of the RGDA/Q112D virus and a weaker interaction with CPSF6 than the RGDA/Q112D virus. The WT virus (black) showed intermediate IFN resistance and intact interactions with MxB, CypA, and CPSF6.