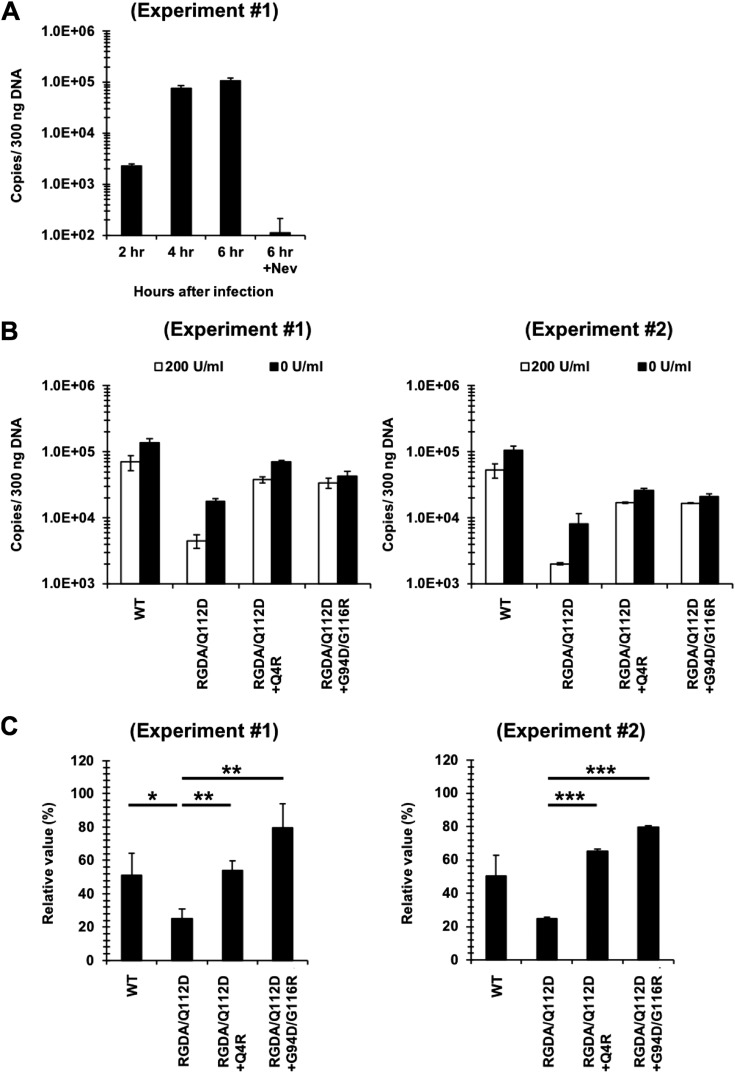
FIG 5.
Steps at or before the second-strand transfer of reverse transcription of the RGDA/Q112D virus were suppressed by IFN-β. (A) Untreated Jurkat cells were infected with the WT virus. DNA extracted at 2, 4, and 6 h after infection was used for PCR to quantify the second-strand transfer products of reverse transcription. Results are shown as the number of copies normalized to the DNA concentrations (number of copies per 300 ng DNA). Cells treated with 5 μM nevirapine (Nev) served as a negative control. Representative data from one of two independent experiments are shown, with error bars denoting the standard deviation (SD) of the mean of duplicate measurements. (B) Jurkat cells treated with 0 or 200 U per ml of IFN-β were infected with the CA mutants. DNA extracted at 6 h after infection was used for PCR to quantify the second-strand transfer products of reverse transcription. Results are shown as the number of copies normalized to the DNA concentrations (number of copies per 300 ng DNA). The results of two independent experiments are shown, with error bars denoting the standard deviation (SD) of the mean of triplicate measurements. (C) The suppressive effect of IFN-β on the generation of second-strand transfer products of reverse transcription at 6 h after infection was evaluated by dividing the copy number of the second-strand transfer products in the presence of 200 U per ml of IFN-β by the copy number in the absence of IFN-β. The results of two independent experiments are shown, with error bars denoting the standard deviation (SD) of the mean of triplicate measurements. ***, P < 0.001; **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05.