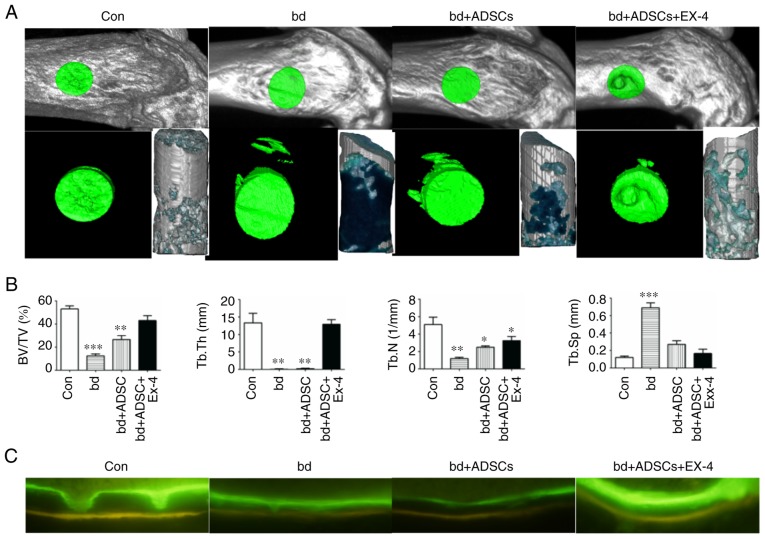
Figure 1.
Exendin-4 facilitates bone defect repair. (A) Representative micro-computed tomography (µCT) scanning results of control mice bone (Con; n=6), defective bone (bd; n=6), defective bone receiving ADSCs (bd+ADSCs; n=6), and defective bone receiving ADSCs and exendin-4 (bd+ADSCs+Ex-4; n=6). (B) Quantitative presentation of microarchitectural parameters of control mice bone (Con; n=6), defective bone (bd; n=6), defective bone receiving ADSCs (bd+ADSCs; n=6), and defective bone receiving ADSCs and exendin-4 (bd+ADSCs+Ex-4; n=6). Error bars represent the mean ± SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001. (C) Calcein and tetracycline double staining of control mice bone (Con; n=6), defective bone (bd; n=6), defective bone receiving ADSCs (bd+ADSCs; n=6), and defective bone receiving ADSCs and exendin-4 (bd+ADSCs+Ex-4; n=6). ADSCs, adipose-derived stem cells.