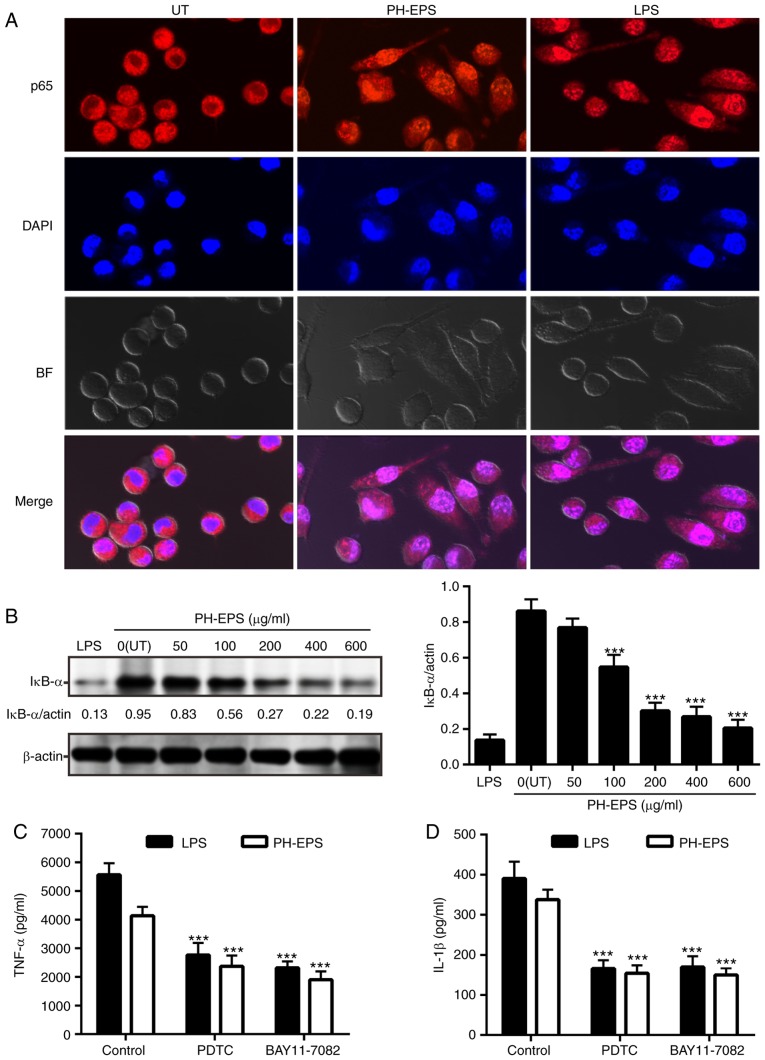
Figure 5.
Effect of PH-EPS on NF-κB signaling pathway. (A) Representative images (magnification, ×600) captured by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Double immunofluorescence staining (NF-κB p65 subunit, red; nucleus, blue) was used to analyze the localization of NFκ-B. (B) IκB-α degradation was analyzed by western blotting. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation of 3 replicates. ***P<0.001 vs. UT group. (C) Effect of NF-κB inhibitors on the TNF-α and (D) IL-1β secretion induced by LPS or PH-EPS. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation of 6 replicates. ***P<0.001 vs. control group. PH-EPS, exopolysaccharides derived from the fungus Paecilomyces lilacinus PH0016; NF, nuclear factor; IκB, inhibitor of κB; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; IL, interleukin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; UT, untreated.