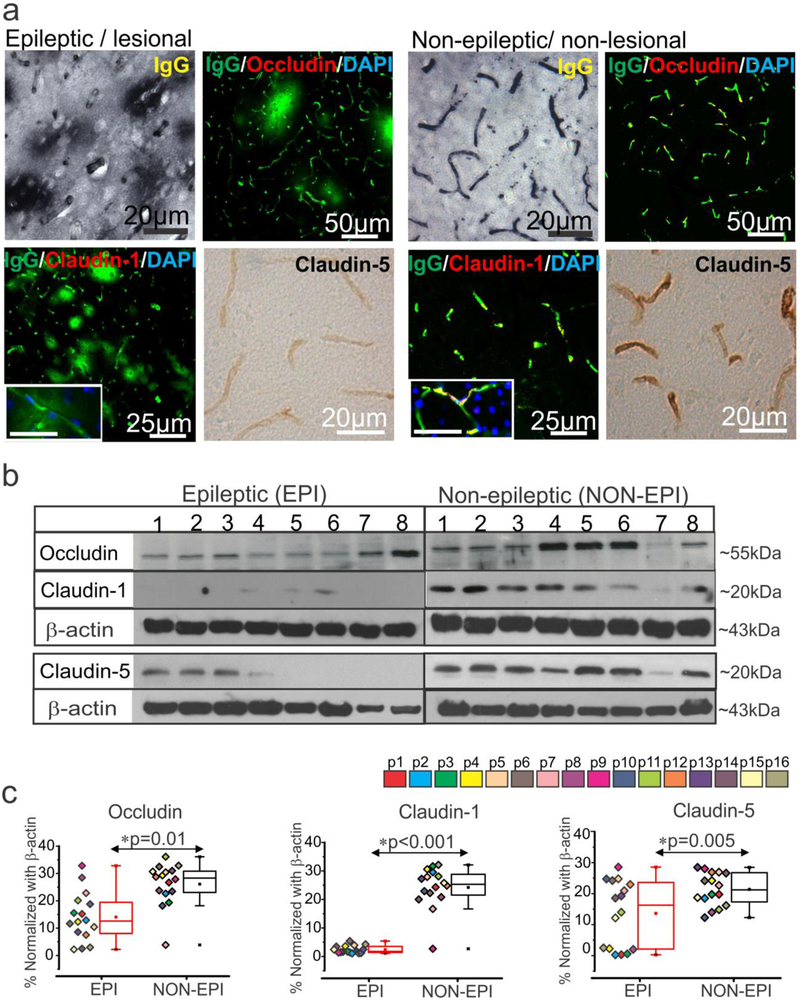
Fig. 1.
BBB leakage and decrease in tight-junction proteins expression predominates in the epileptogenic region.
(a) Representative images of immunostaining shows increase in IgG extravagation to the brain parenchyma across the brain vasculature and a corresponding decrease in expression of the tight-junction proteins claudin-1, claudin-5, and occludin in EPI/lesional region (n = 6, in triplicates) compared to NON-EPI /non-lesional region. Inset scale bars represents 20 μm. (b, c) Western blot analysis confirms decrease in the level of tight-junction protein expression, occludin (*p = 0.01), claudin-1 (*p < 0.001) and claudin-5 (*p = 0.005) in brain tissue specimens obtained from EPI vs. NON-EPI regions. Representative westerns depicting expression of tight-junction proteins (n = 8 subjects) with β-actin used as loading control (b). Densitometries for individual protein bands (from n = 16 subjects, with color codes p1-p16 depicting each subject) normalized with β-actin (c). Results are expressed as mean ± SEM by non-parametric analysis for paired samples Wilcoxon signed rank test for direct comparison of two population of data.