Fig. 4.
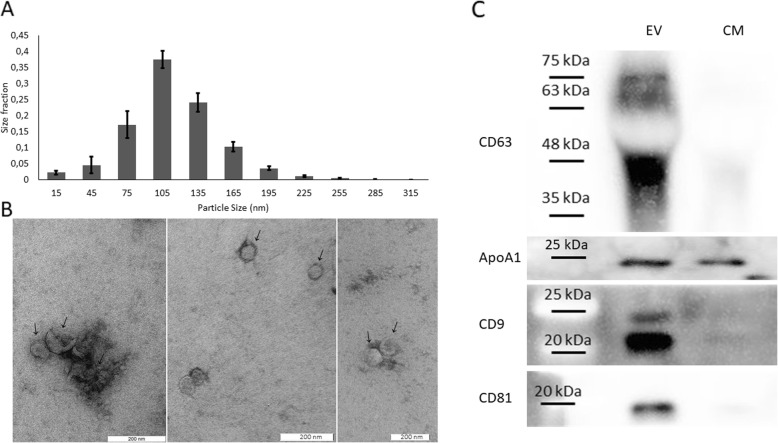
Confirmation of trophoblast spheroid derived nanoparticles as extracellular vesicles (EVs). a Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) of trophoblast spheroid derived extracellular vesicles (EVs). Number and size profiles of EVs were analysed using ZetaView™ nanoparticle analyser. The profile exhibits a typical distribution of particles mostly less than 200 nm. Data is presented as mean ± SEM. b The transmission electron microscopy for EVs’ morphology. EVs visualized after staining in 2% uranyl acetate following by uranyl oxalate and methylcellulose. Scale bar = 200 nm. Classic morphological characteristics such as uniform shape, clearly discernible lipid bilayers and “cup shape” is observed. c Western blot analysis of trophoblast spheroid derived EVs (EV) and trophoblast spheroid conditioned media (CM). Specific protein markers for EVs (CD63, CD9 and CD81) are enriched in EV samples while negative control Apo A-I is not enriched