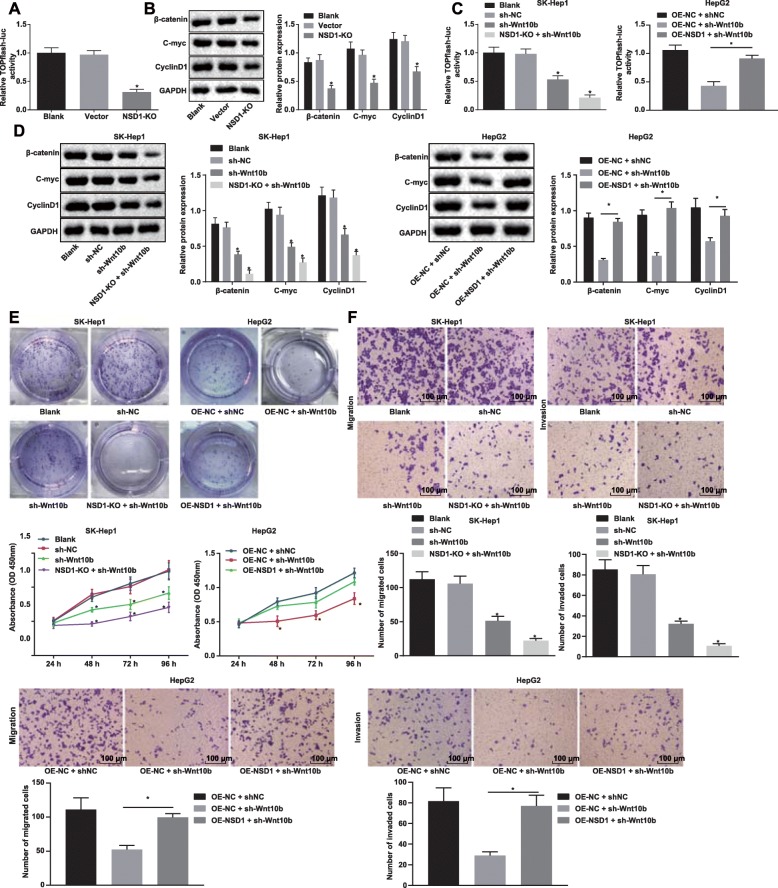
Fig. 4.
Knockout of NSD1 inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to suppress HCC cell proliferation, migration and invasion. a, Relative TOPFlash luciferase activity after NSD1 knockout. b, Protein expression of key proteins β-catenin, C-myc and CyclinD1 in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway normalized to GAPDH after Wnt10b knockout determined by Western blot analysis. c, Relative TOPFlash luciferase activity after Wnt10b silencing, NSD1 silencing or both NSD1 overexpression and Wnt10b silencing. d, Protein expression of Wnt10b and key proteins, β-catenin, C-myc and CyclinD1 in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway normalized to GAPDH determined by Western blot analysis. e, Proliferation ability of cells in different groups measured by CCK-8 and monoclonal formation assays. f, Migration and invasion ability of cells in differently groups detected by Transwell assay (× 100). * p < 0.05 vs. the blank group (SK-Hep1/HepG2 cells without any treatment). Data (mean ± s.d.) among multiple groups were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test, while data at different time points were analyzed by repeated measures ANOVA, followed by the Bonferroni’s post-hoc test. The experiment was repeated 3 times independently