Fig. 3.
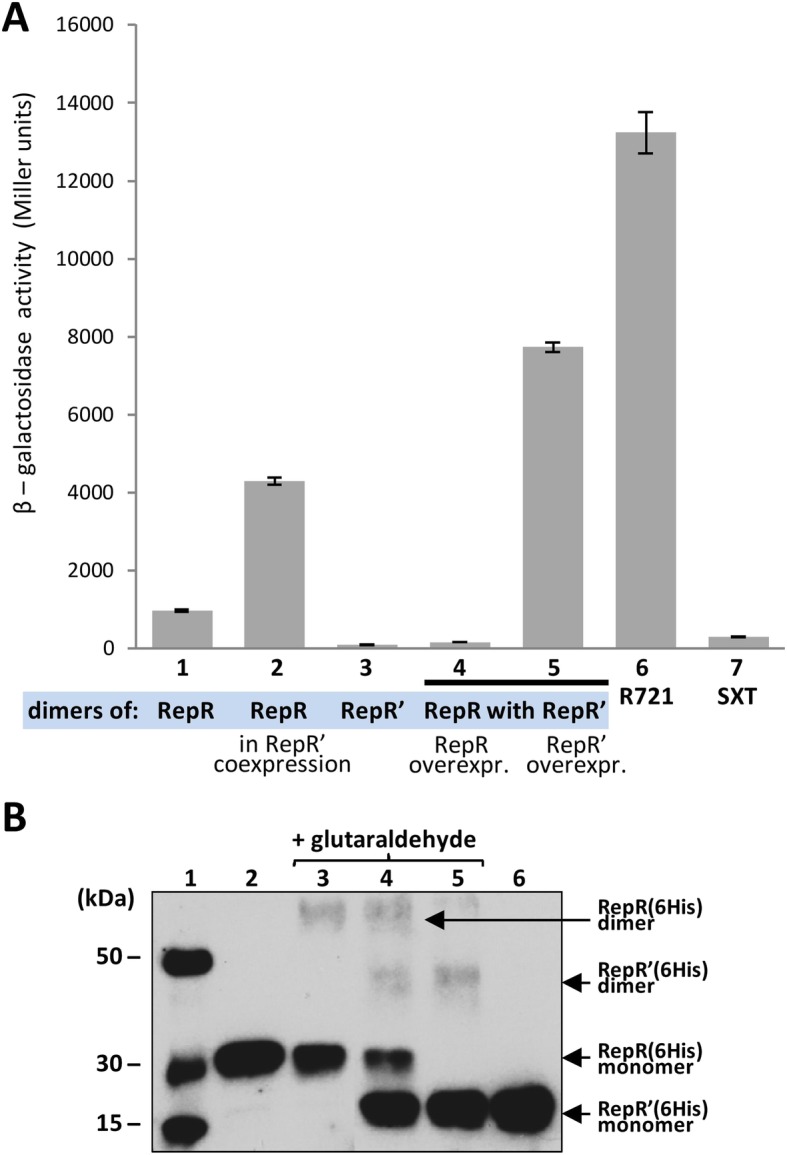
Direct interactions of RepR and RepR’ proteins. a In vivo interactions of the RepR and RepR’ proteins determined using a bacterial two-hybrid system. β-Galactosidase activity in E. coli R721 strains expressing N-terminally fused proteins: (1) RepR alone, (2) RepR co-expressed with wt RepR’, (3) RepR’ alone, (4) RepR plus RepR’ in the presence of RepR overexpression, (5) RepR plus RepR’ in the presence of RepR’ overexpression, (6) plasmid-less E. coli strain R721 as a negative control, 7. SXT – positive control system (toxin and antitoxin proteins of the Vibrio cholerae SXT element addiction system) [28]. A decrease in β-galactosidase activity relative to the negative control indicates the formation of protein dimers. b In vitro interactions of the RepR(6His) and RepR’(6His) proteins determined using glutaraldehyde cross-linking: (1) protein molecular-weight size marker, (2) RepR(6His), (3) RepR(6His) incubated with glutaraldehyde, (4) both RepR(6His) and RepR’(6His) incubated with glutaraldehyde, (5) RepR’(6His) incubated with glutaraldehyde, (6) RepR(6His)
