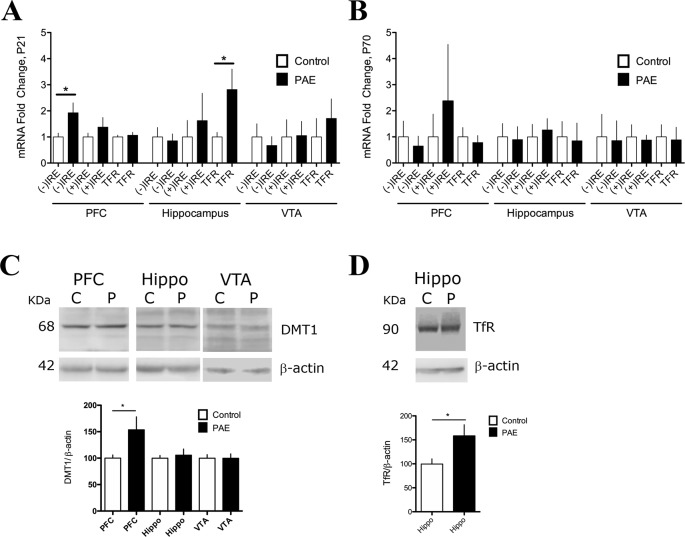
Figure 1.
Prenatal ethanol exposure (PAE) affected messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein expression of iron transporters divalent metal transporter (DMT1) and transferrin receptor (TfR) in rat brain. (A) Relative mRNA expression of DMT1 isoforms [(−) IRE and (+) IRE], and TFR in the prefrontal cortex (PFC), hippocampus, and ventral tegmental area (VTA) of P21 PAE rats compared to respective brain areas of P21 controls rats. Graph A shows mRNA expression (fold change) in controls and PAE calculated using formula 1 and 2 (Material and methods) with means ± SEM. *p < 0.05 for comparison by Mann–Whitney. N 5. (B) Relative mRNA expression of the same genes and brain areas of PAE and control rats as A, but for ages P70–78. Graph B shows mRNA expression (fold) in controls and PAE, calculated using formula 1 and 2 (Material and methods) with means ± SEM. *p < 0.05 for comparison by Mann–Whitney. N 5 litters. (C) Western blot analysis of DMT1 expression in control (C) and PAE (P) P70–78 rats in the PFC, hippocampus (Hippo), and VTA. N = 10 litters. (D) Western blot analysis of TfR expression in control (C) and PAE (P) of P21. N = 6 litters. DMT1 and TfR proteins were immuno-detected using specific antibodies and normalized to β-actin (42 kDa). Graphs in C and D show means ± SEM, and *p < 0.05 for the indicated comparisons by Mann–Whitney test.