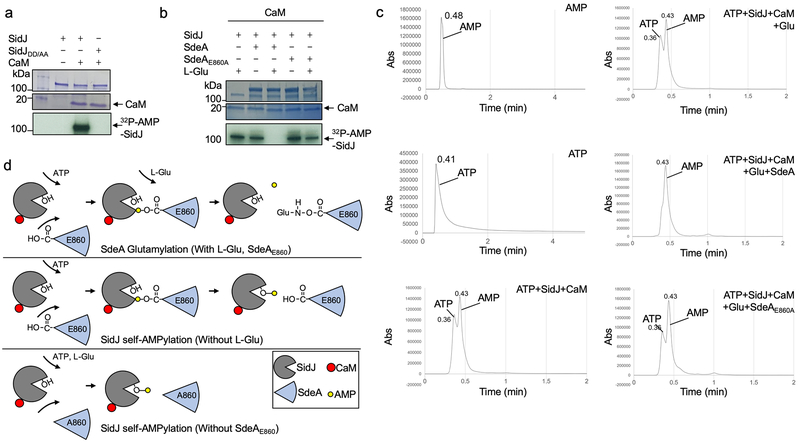
Extended Data Fig. 7. The mechanism of SidJ induced CaM dependent self-AMPlyation and SdeA glutamylation.
a. SidJ induces self-AMPylation in a CaM dependent manner. SidJ was incubated with 32P-α-ATP, Mg2+, with or without CaM for 2 h at 37°C. After separation by SDS-PAGE, the incorporation of 32P-α-ATP was detected by autoradiography.
b. SdeA glutamylation by SidJ interferes with SidJ self-AMPylation. SidJ was incubated with 32P-α-ATP, Mg2+, CaM for 2 h at 37°C. When needed L-Glu, SdeA, SdeAE860A were supplemented. After separation by SDS-PAGE, the incorporation of 32P-α-ATP was detected by autoradiography.
c. SdeA glutamylation by SidJ accelerates ATP hydrolysis and AMP release. SidJ was incubated with indicated components for 2 h at 37°C. Samples were analyzed by HPLC. AMP and ATP were used as standard. In panels a-c, data shown were one representative from at least three independent experiments that had similar results.
d. Schematic model of SidJ induced glutamylation and AMPylation. SidJ incudes glutamylation on SdeAE860 when ATP and L-Glu are supplemented in reaction. In reactions missing L-Glu or modifiable SdeA, SidJ induces self-AMPylation.